Molecular pathogenesis of Wilson and Menkes disease: correlation of mutations with molecular defects and disease phenotypes
- PMID: 17717039
- PMCID: PMC2752173
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2007.052746
Molecular pathogenesis of Wilson and Menkes disease: correlation of mutations with molecular defects and disease phenotypes
Abstract
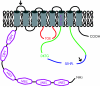
The trace metal copper is essential for a variety of biological processes, but extremely toxic when present in excessive amounts. Therefore, concentrations of this metal in the body are kept under tight control. Central regulators of cellular copper metabolism are the copper-transporting P-type ATPases ATP7A and ATP7B. Mutations in ATP7A or ATP7B disrupt the homeostatic copper balance, resulting in copper deficiency (Menkes disease) or copper overload (Wilson disease), respectively. ATP7A and ATP7B exert their functions in copper transport through a variety of interdependent mechanisms and regulatory events, including their catalytic ATPase activity, copper-induced trafficking, post-translational modifications and protein-protein interactions. This paper reviews the extensive efforts that have been undertaken over the past few years to dissect and characterise these mechanisms, and how these are affected in Menkes and Wilson disease. As both disorders are characterised by an extensive clinical heterogeneity, we will discus how the underlying genetic defects correlate with the molecular functions of ATP7A and ATP7B and with the clinical expression of these disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
[From gene to disease: copper-transporting P ATPases alteration].Pathol Biol (Paris). 2009 May;57(3):272-9. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2008.09.004. Epub 2008 Nov 28. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2009. PMID: 19046832 French.
-
The Menkes and Wilson disease genes counteract in copper toxicosis in Labrador retrievers: a new canine model for copper-metabolism disorders.Dis Model Mech. 2016 Jan;9(1):25-38. doi: 10.1242/dmm.020263. Dis Model Mech. 2016. PMID: 26747866 Free PMC article.
-
Copper transporting P-type ATPases and human disease.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2002 Oct;34(5):333-8. doi: 10.1023/a:1021293818125. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2002. PMID: 12539960 Review.
-
Clusterin (apolipoprotein J), a molecular chaperone that facilitates degradation of the copper-ATPases ATP7A and ATP7B.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 25;286(12):10073-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.190546. Epub 2011 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21242307 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking of the copper-ATPases, ATP7A and ATP7B: role in copper homeostasis.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007 Jul 15;463(2):149-67. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2007.04.021. Epub 2007 May 7. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007. PMID: 17531189 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic Analysis and Insights Into the Mutation Spectrum and Ethnic Differences in ATP7B Mutations Associated With Wilson Disease.Biomark Insights. 2024 Nov 4;19:11772719241297169. doi: 10.1177/11772719241297169. eCollection 2024. Biomark Insights. 2024. PMID: 39502306 Free PMC article.
-
Multipoint genome-wide linkage scan for nonword repetition in a multigenerational family further supports chromosome 13q as a locus for verbal trait disorders.Hum Genet. 2016 Dec;135(12):1329-1341. doi: 10.1007/s00439-016-1717-z. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27535846 Free PMC article.
-
ATP7A Clinical Genetics Resource - A comprehensive clinically annotated database and resource for genetic variants in ATP7A gene.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Sep 2;18:2347-2356. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.08.021. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 32994893 Free PMC article.
-
The neuropsychiatry of hyperkinetic movement disorders: insights from neuroimaging into the neural circuit bases of dysfunction.Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2013 Aug 26;3:tre-03-175-4242-1. doi: 10.7916/D8SN07PK. eCollection 2013. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2013. PMID: 24032090 Free PMC article.
-
Novel techniques and newer markers for the evaluation of "proximal tubular dysfunction".Int Urol Nephrol. 2011 Dec;43(4):1107-15. doi: 10.1007/s11255-011-9914-0. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Int Urol Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21360162 Review.
References
-
- Culotta V C, Gitlin J D. Disorders of copper transport. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, et al eds. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. New York: McGraw‐Hill, 200123105–3126.
-
- Stohs S J, Bagchi D. Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 199518321–336. - PubMed
-
- Menkes J H, Alter M, Steigleder G K, Weakley D R, Sung J H. A sex‐linked recessive disorder with retardation of growth, peculiar hair, and focal cerebral and cerebellar degeneration. Pediatrics 196229764–779. - PubMed
-
- Wilson S A K. Progressive lenticular degeneration: A familial nervous disease associated with cirrhosis of the liver. Brain 191234295–509. - PubMed
-
- Tanner M S. Role of copper in Indian childhood cirrhosis. Am J Clin Nutr 199867(Suppl)1074–81S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous