Prolonged attenuation of amygdala-kindled seizure measures in rats by convection-enhanced delivery of the N-type calcium channel antagonists omega-conotoxin GVIA and omega-conotoxin MVIIA
- PMID: 17717191
- PMCID: PMC2257985
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.107.125047
Prolonged attenuation of amygdala-kindled seizure measures in rats by convection-enhanced delivery of the N-type calcium channel antagonists omega-conotoxin GVIA and omega-conotoxin MVIIA
Abstract
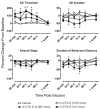
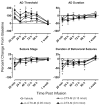
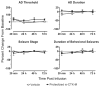
Convection-enhanced delivery (CED) permits the homogeneous distribution of therapeutic agents throughout localized regions of the brain parenchyma without causing tissue damage as occurs with bolus injection. Here, we examined whether CED infusion of the N-type calcium channel antagonists omega-conotoxin GVIA (omega-CTX-G) and omega-conotoxin MVIIA (omega-CTX-M) can attenuate kindling measures in fully amygdala-kindled rats. Rats were implanted with a combination infusion cannula-stimulating electrode assembly into the right basolateral amygdala. Fully kindled animals received infusions of vehicle, omega-CTX-G (0.005, 0.05, and 0.5 nmol), omega-CTX-M (0.05, 0.15, and 0.5 nmol), proteolytically inactivated omega-CTX-M (0.5 nmol), or carbamazepine (500 nmol) into the stimulation site. CED of omega-CTX-G and omega-CTX-M over a 20-min period resulted in a dose-dependent increase in the afterdischarge threshold and a decrease in the afterdischarge duration and behavioral seizure score and duration during a period of 20 min to 1 week after the infusion, indicating an inhibitory effect on the triggering and expression of kindled seizures. The protective effects of omega-conotoxins reached a maximum at 48 h postinfusion, and then they gradually resolved over the next 5 days. In contrast, carbamazepine was active at 20 min but not at 24 h after the infusion, whereas CED of vehicle or inactivated omega-CTX-M had no effect. Except for transient tremor in some rats receiving the highest toxin doses, no adverse effects were observed. These results indicate that local CED of high-molecular-weight presynaptic N-type calcium channel blockers can produce long-lasting inhibition of brain excitability and that they may provide prolonged seizure protection in focal seizure disorders.
Figures






Similar articles
-
omega-Conotoxin MVIIA inhibits amygdaloid kindled seizures in Sprague-Dawley rats.Neurosci Lett. 2007 Feb 14;413(2):163-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.11.049. Epub 2007 Jan 4. Neurosci Lett. 2007. PMID: 17207931
-
Long-lasting attenuation of amygdala-kindled seizures after convection-enhanced delivery of botulinum neurotoxins a and B into the amygdala in rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Sep;346(3):528-34. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.205070. Epub 2013 Jun 14. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013. PMID: 23772062 Free PMC article.
-
Actions of intrathecal omega-conotoxins CVID, GVIA, MVIIA, and morphine in acute and neuropathic pain in the rat.Eur J Pharmacol. 2002 Sep 20;451(3):279-86. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(02)02247-1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12242089
-
Effects of N-, P- and Q-type neuronal calcium channel antagonists on mammalian peripheral neurotransmission.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Sep;119(1):49-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15676.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8872356 Free PMC article.
-
Convection-enhanced delivery in the treatment of epilepsy.Neurotherapeutics. 2009 Apr;6(2):344-51. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2009.01.017. Neurotherapeutics. 2009. PMID: 19332329 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology for delivery of drugs to the brain for epilepsy.Neurotherapeutics. 2009 Apr;6(2):323-36. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2009.01.018. Neurotherapeutics. 2009. PMID: 19332327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TAT-Modified ω-Conotoxin MVIIA for Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier.Mar Drugs. 2019 May 12;17(5):286. doi: 10.3390/md17050286. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31083641 Free PMC article.
-
Convection-enhanced delivery of botulinum toxin serotype A into the nonhuman primate cisterna magna and hippocampus.J Neurosurg. 2019 Jul 19;133(2):588-595. doi: 10.3171/2019.4.JNS19744. Print 2020 Aug 1. J Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31323637 Free PMC article.
-
Pro- and Anticonvulsant Effects of the Ant Dinoponera quadriceps (Kempf) Venom in Mice.Neotrop Entomol. 2015 Aug;44(4):410-7. doi: 10.1007/s13744-015-0292-7. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Neotrop Entomol. 2015. PMID: 26045053
-
Convection-enhanced delivery for the treatment of brain tumors.Expert Rev Neurother. 2009 Oct;9(10):1519-27. doi: 10.1586/ern.09.99. Expert Rev Neurother. 2009. PMID: 19831841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albertson TE, Joy RM, Stark LG. A pharmacological study in the kindling model of epilepsy. Neuropharmacology. 1984;23:1117–1123. - PubMed
-
- Barcia JA, Rubio P, Alos M, Serralta A, Belda V. Anticonvulsant and neurotoxic effects of intracerebroventricular injection of phenytoin, phenobarbital and carbamazepine in an amygdala-kindling model of epilepsy in the rat. Epilepsy Res. 1999;33:159–167. - PubMed
-
- Berg AT, Vickrey BG, Langfitt JT, Sperling MR, Walczak TS, Shinnar S, Bazil CW, Pacia SV, Spencer SS, Multicenter Study of Epilepsy Surgery The multicenter study of epilepsy surgery: recruitment and selection for surgery. Epilepsia. 2003;44:1425–1433. - PubMed
-
- Boulton CL, O’Shaughnessy CT. The effect of calcium channel antagonists on spontaneous and evoked epileptiform activity in the rat neocortex in vitro. Eur J Neurosci. 1991;3:992–1000. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

