Mice lacking NKCC1 have normal olfactory sensitivity
- PMID: 17719611
- PMCID: PMC2257478
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.07.011
Mice lacking NKCC1 have normal olfactory sensitivity
Abstract
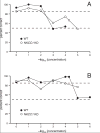
When olfactory receptor neurons respond to odors, a depolarizing Cl(-) efflux is a substantial part of the response. This requires that the resting neuron accumulate Cl(-) against an electrochemical gradient. In isolated olfactory receptor neurons, the Na(+)+K(+)+2Cl(-) cotransporter NKCC1 is essential for Cl(-) accumulation. However, in intact epithelium, a robust electrical olfactory response persists in mice lacking NKCC1. To determine whether NKCC1 is required for normal olfactory sensitivity, olfactory sensitivity was compared between knockout (KO) mice carrying a null mutation for NKCC1 and wild-type (WT) littermates. Using operant behavioral techniques, olfactory sensitivity was measured using a commercial liquid-dilution olfactometer. Detection thresholds for the simple odorants cineole, 1-heptanol, and 1-propanol were compared in KO and WT animals. Regardless of the stimulus conditions employed, no systematic differences in behavioral thresholds were evident between KO and WT animals. We conclude that NKCC1 is not required for normal olfactory sensitivity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ion transporter NKCC1, modulator of neurogenesis in murine olfactory neurons.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 10;290(15):9767-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.640656. Epub 2015 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25713142 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of neuronal chloride accumulation in intact mouse olfactory epithelium.J Physiol. 2007 Sep 15;583(Pt 3):1005-20. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.129601. Epub 2007 Jul 26. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17656441 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal chloride accumulation in olfactory epithelium of mice lacking NKCC1.J Neurophysiol. 2006 Mar;95(3):2003-6. doi: 10.1152/jn.00962.2005. Epub 2005 Nov 30. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16319203 Free PMC article.
-
The ins and outs of intracellular chloride in olfactory receptor neurons.Neuron. 2005 Feb 17;45(4):481-2. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.02.002. Neuron. 2005. PMID: 15721233 Review.
-
Anoctamin 2/TMEM16B: a calcium-activated chloride channel in olfactory transduction.Exp Physiol. 2012 Feb;97(2):193-9. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2011.058230. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Exp Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21890523 Review.
Cited by
-
Whole mount labeling of cilia in the main olfactory system of mice.J Vis Exp. 2014 Dec 27;(94):52299. doi: 10.3791/52299. J Vis Exp. 2014. PMID: 25590569 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+-activated Cl− currents are dispensable for olfaction.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Jun;14(6):763-9. doi: 10.1038/nn.2821. Epub 2011 Apr 24. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21516098
-
Modulation of chloride homeostasis by inflammatory mediators in dorsal root ganglion neurons.Mol Pain. 2008 Aug 12;4:32. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-4-32. Mol Pain. 2008. PMID: 18700020 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic-nucleotide-gated cation current and Ca2+-activated Cl current elicited by odorant in vertebrate olfactory receptor neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Oct 4;113(40):11078-11087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1613891113. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27647918 Free PMC article.
-
Ion transporter NKCC1, modulator of neurogenesis in murine olfactory neurons.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 10;290(15):9767-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.640656. Epub 2015 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25713142 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

