Magnesium sulfate diminishes the effects of amide local anesthetics in rat sciatic-nerve block
- PMID: 17720112
- PMCID: PMC2001297
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rapm.2007.03.008
Magnesium sulfate diminishes the effects of amide local anesthetics in rat sciatic-nerve block
Abstract
Background and objectives: Magnesium sulfate (MgSO(4)) is well known as an antagonist of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors and was used for intrathecal analgesia a century ago. However, the effects of MgSO(4) combined with local anesthetics (LAs) on peripheral nerves are unclear. We tested the hypothesis that MgSO(4) could be used as an adjuvant to prolong and intensify conduction block by amide-type LAs in a rat sciatic-nerve block model. Further, the mechanism of possible synergy between LAs and MgSO(4) was investigated in whole-cell mode patch-clamp experiments.
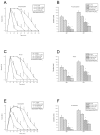
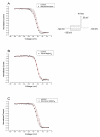
Methods: Sciatic nerves were exposed to 2%/73.9 mM lidocaine, 0.25%/7.7 mM bupivacaine, and 0.5%/15.4 mM ropivacaine, with or without addition of 1.25%, 2.5%, or 5% MgSO(4)/50.7 mM, and nerve block characteristics were assessed. To elucidate the LA-MgSO(4) interaction, voltage-dependent inactivation curves were determined in cultured rat GH(3) cells that expressed neuronal Na(+) channels.
Results: Unexpectedly, the addition of MgSO(4) overall significantly shortened the duration of block by lidocaine, bupivacaine, and ropivacaine. The steady-state inactivation of Na(+) channels in the presence of 300 muM lidocaine was almost unchanged by the addition of 10 mM MgSO(4), indicating that MgSO(4) does not affect the potency of lidocaine toward the inactivated Na(+) channel.
Conclusions: MgSO(4) coadministered with amide-type LAs shortened the duration of sciatic-nerve block in rats. Therefore, it does not seem to be useful as an adjuvant for peripheral-nerve block. The mechanism of this observed antagonism is unclear but appears to be independent of the action of LAs and MgSO(4) at the LA receptor within the Na(+) channel.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Calcium chloride prolongs the effects of lidocaine and bupivacaine in rat sciatic nerve.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2009 Jul-Aug;34(4):333-9. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e3181ac7f49. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2009. PMID: 19574866
-
Local anesthetic sciatic nerve block and nerve fiber damage in diabetic rats.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2010 Jul-Aug;35(4):343-50. doi: 10.1097/aap.0b013e3181e82df0. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2010. PMID: 20607875
-
Levobupivacaine versus ropivacaine for sciatic nerve block in the rat.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2003 Jul-Aug;28(4):294-303. doi: 10.1016/s1098-7339(03)00188-3. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2003. PMID: 12945022
-
Fundamental properties of local anesthetics: half-maximal blocking concentrations for tonic block of Na+ and K+ channels in peripheral nerve.Anesth Analg. 1998 Oct;87(4):885-9. doi: 10.1097/00000539-199810000-00026. Anesth Analg. 1998. PMID: 9768788
-
Efficacy of lidocaine or bupivacaine combined with ephedrine in rat sciatic nerve block.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2006 Jan-Feb;31(1):14-8. doi: 10.1016/j.rapm.2005.08.008. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2006. PMID: 16418019
Cited by
-
To evaluate the efficacy of intrathecal magnesium sulphate for hysterectomy under subarachnoid block with bupivacaine and fentanyl: A prospective randomized double blind clinical trial.Saudi J Anaesth. 2012 Jul;6(3):254-8. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.101217. Saudi J Anaesth. 2012. PMID: 23162399 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Magnesium Sulfate and Ketamine with Ropivacaine in Supraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Anesth Essays Res. 2020 Jan-Mar;14(1):143-148. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_96_19. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Anesth Essays Res. 2020. PMID: 32843808 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of magnesium as an adjuvant to bupivacaine in 3-in-1 nerve block for arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament repair.Indian J Anaesth. 2016 Jul;60(7):491-5. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.186018. Indian J Anaesth. 2016. PMID: 27512165 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy of ropivacaine and levobupivacaine in combined femoral and lateral femoral cutaneous nerve block with adjuvant magnesium for post-operative analgesia.Indian J Anaesth. 2016 Aug;60(8):584-9. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.187794. Indian J Anaesth. 2016. PMID: 27601742 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Ropivacaine Addition to Intrathecal Morphine for Pain Management in Intractable Cancer.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:439014. doi: 10.1155/2015/439014. Epub 2015 Oct 18. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26556955 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Kohane DS, Smith SE, Louis DN, Colombo G, Ghoroghchian P, Hunfeld NG, Berde CB, Langer R. Prolonged duration local anesthesia from tetrodotoxin-enhanced local anesthetic microspheres. Pain. 2003;104:415–421. - PubMed
-
- Barnet CS, Tse JY, Kohane DS. Site 1 sodium channel blockers prolong the duration of sciatic nerve blockade from tricyclic antidepressants. Pain. 2004;110:432–438. - PubMed
-
- Hung YC, Kau YC, Zizza AM, Edrich T, Zurakowski D, Myers RR, Wang GK, Gerner P. Ephedrine blocks rat sciatic nerve in vivo and sodium channels in vitro. Anesthesiology. 2005;103:1246–1252. - PubMed
-
- Mayer ML, Westbrook GL, Guthrie PB. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984;309:261–263. - PubMed
-
- Meltzer SJ, Auer J. Physiological and pharmacological studies on magnesium salts. III. Narcotizing effect of magnesium salts upon nerve fibers. Am J Physiol. 1906;16:233–251.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
