Large-scale, saturating insertional mutagenesis of the mouse genome
- PMID: 17720809
- PMCID: PMC1964832
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700608104
Large-scale, saturating insertional mutagenesis of the mouse genome
Abstract
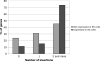
We describe the construction of a large-scale, orderly assembly of mutant ES cells, generated with retroviral insertions and having mutational coverage in >90% of mouse genes. We also describe a method for isolating ES cell clones with mutations in specific genes of interest from this library. This approach, which combines saturating random mutagenesis with targeted selection of mutations in the genes of interest, was successfully applied to the gene families of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and nuclear receptors. Mutant mouse strains in 60 different GPCRs were generated. Applicability of the technique for the GPCR genes, which on average represent fairly small targets for insertional mutagenesis, indicates the general utility of our approach for the rest of the genome. The method also allows for increased scale and automation for the large-scale production of mutant mice, which could substantially expedite the functional characterization of the mouse genome.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: A.G., M.P., L.M., H.Z., G.G., A.R., I.D., A.E., S.M., C.N., E.F., J.B., D.K.V., and G.A.G. are or were employees of privately owned Omeros Corporation and declare competing financial interests.
Figures
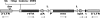



Similar articles
-
Selection of targeted mutants from a library of randomly mutagenized ES cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;693:283-94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-974-1_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21080287
-
Disruption and sequence identification of 2,000 genes in mouse embryonic stem cells.Nature. 1998 Apr 9;392(6676):608-11. doi: 10.1038/33423. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9560157
-
A recessive genetic screen for host factors required for retroviral infection in a library of insertionally mutated Blm-deficient embryonic stem cells.Genome Biol. 2007;8(4):R48. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-4-r48. Genome Biol. 2007. PMID: 17407599 Free PMC article.
-
Insertional versus targeted mutagenesis in mice.New Biol. 1991 Nov;3(11):1025-34. New Biol. 1991. PMID: 1777476 Review.
-
Gene targeting in murine embryonic stem cells: introduction of specific alterations into the mammalian genome.Genet Anal Tech Appl. 1990 Dec;7(8):219-27. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(90)90004-y. Genet Anal Tech Appl. 1990. PMID: 2091698 Review.
Cited by
-
Human pluripotent stem cells: an emerging model in developmental biology.Development. 2013 Feb;140(4):705-17. doi: 10.1242/dev.086165. Development. 2013. PMID: 23362344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kiss of the mutant mouse: how genetically altered mice advanced our understanding of kisspeptin's role in reproductive physiology.Endocrinology. 2012 Nov;153(11):5119-29. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1494. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 23011921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene trap mutagenesis in the mouse.Methods Enzymol. 2010;477:243-69. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(10)77013-0. Methods Enzymol. 2010. PMID: 20699145 Free PMC article.
-
A simplified transposon mutagenesis method to perform phenotypic forward genetic screens in cultured cells.BMC Genomics. 2019 Jun 17;20(1):497. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5888-6. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31208320 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale gene trapping in C57BL/6N mouse embryonic stem cells.Genome Res. 2008 Oct;18(10):1670-9. doi: 10.1101/gr.078352.108. Epub 2008 Sep 17. Genome Res. 2008. PMID: 18799693 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

