Mucocutaneous lesions of Behcet's disease
- PMID: 17722228
- PMCID: PMC2628050
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.4.573
Mucocutaneous lesions of Behcet's disease
Abstract
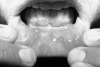
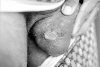
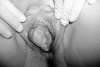
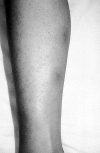
Behcet's disease is particularly prevalent in "Silk Route" populations, but it has a global distribution. The diagnosis of the disease is based on clinical criteria as there is as yet no pathognomonic test, and mucocutaneous lesions, which figure prominently in the presentation and diagnosis, may be considered the diagnostic hallmarks. Among the internationally accepted criteria, painful oral and genital ulcers, cutaneous vasculitic lesions and reactivity of the skin to needle prick or injection (the pathergy reaction) are considered hallmarks of Behcet's disease, and often precede other manifestations. Their recognition may permit earlier diagnosis and treatment, with salutary results. This paper describes the various lesions that constitute the syndrome and focuses on those that may be considered characteristic.
Figures


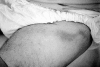

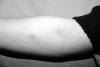

References
-
- Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behçet's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1284–1291. - PubMed
-
- Ehrlich GE, Kajani M, Schwartz IR, McAlack RF. Further studies of platelet rosettes around granulocytes in Behçet's syndrome. Inflammation. 1975;1:223–225. - PubMed
-
- Lehner T. Immunopathogenesis of Behçet's disease. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 1999;150:483–487. - PubMed
-
- Alpsoy E, Yılmaz E, Coşkun M, Savaş A, Yeğin O. HLA antigens and linkage disequilibrium patterns in Turkish Behçet's patients. J Dermatol. 1998;25:158–162. - PubMed
-
- Alpsoy E, Çayırlı C, Er H, Yılmaz E. The levels of plasma interleukin-2 and soluble interleukin-2R in Behçet's disease: as a marker of disease activity. J Dermatol. 1998;25:513–516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

