Paraspinal abscess communicated with epidural abscess after extra-articular facet joint injection
- PMID: 17722247
- PMCID: PMC2628056
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.4.711
Paraspinal abscess communicated with epidural abscess after extra-articular facet joint injection
Abstract
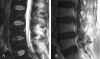
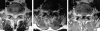
Facet joint injection is considered to be a safe procedure. There have been some reported cases of facet joint pyogenic infection and also 3 cases of facet joint infection spreading to paraspinal muscle and epidural space due to intra-articular injections. To the author's knowledge, paraspinal and epidural abscesses after facet joint injection without facet joint pyogenic infection have not been reported. Here we report a case in which extra-articular facet joint injection resulted in paraspinal and epidural abscesses without facet joint infection. A 50-year-old man presenting with acute back pain and fever was admitted to the hospital. He had the history of diabetes mellitus and had undergone the extra-articular facet joint injection due to a facet joint syndrome diagnosis at a private clinic 5 days earlier. Physical examination showed tenderness over the paraspinal region. Magnetic resonance image (MRI) demonstrated the paraspinal abscess around the fourth and fifth spinous processes with an additional epidural abscess compressing the thecal sac. The facet joints were preserved. The laboratory results showed a white blood cell count of 14.9 x 10(9) per liter, an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 52 mm/hour, and 10.88 mg/dL of C-reactive protein. Laminectomy and drainage were performed. The pus was found in the paraspinal muscles, which was communicated with the epidural space through a hole in the ligamentum flavum. Cultures grew Staphylococcus aureus. Paraspinal abscess communicated with epidural abscess is a rare complication of extra-articular facet joint injection demonstrating an abscess formation after an invasive procedure near the spine is highly possible.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hematogenous pyogenic facet joint infection.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001 Jul 15;26(14):1570-6. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200107150-00014. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. PMID: 11462088
-
Hematogenous pyogenic facet joint infection of the subaxial cervical spine. A report of two cases and review of the literature.J Neurosurg. 2001 Jul;95(1 Suppl):135-8. doi: 10.3171/spi.2001.95.1.0135. J Neurosurg. 2001. PMID: 11453416
-
Septic arthritis of bilateral lumbar facet joints: report of a case with MRI findings in the early stage.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003 May 15;28(10):E198-202. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000062006.92938.41. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003. PMID: 12768159
-
Lumbar facet joint infection associated with epidural and paraspinal abscess: a case report with review of the literature.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005 Oct;18(5):458-61. doi: 10.1097/01.bsd.0000159036.42989.93. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005. PMID: 16189461 Review.
-
Septic arthritis of a lumbar facet joint case report and review of the literature.Acta Orthop Belg. 2004 Jun;70(3):290-4. Acta Orthop Belg. 2004. PMID: 15287413 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Sternoclavicular Joint Sepsis With Medial Clavicle Osteomyelitis (Staphylococcus aureus) and Cervical-Thoracic Epidural Phlegmon in an Adult Female With No Apparent Risk Factors.Cureus. 2023 Mar 7;15(3):e35870. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35870. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37033534 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriasis vulgaris of the skin caused a L3-L4 lumbar epidural spinal abscess.Surg Neurol Int. 2024 Apr 12;15:125. doi: 10.25259/SNI_88_2024. eCollection 2024. Surg Neurol Int. 2024. PMID: 38741987 Free PMC article.
-
Generalized infection following facet joint injection -A case report-.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010 Apr;58(4):401-4. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2010.58.4.401. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010. PMID: 20508800 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Corticosteroid Injection Timing on Infection Rates Following Spine Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Global Spine J. 2022 Sep;12(7):1524-1534. doi: 10.1177/21925682211026630. Epub 2021 Sep 26. Global Spine J. 2022. PMID: 34569332 Free PMC article.
-
FactFinders for patient safety: Use of sterile gloves for interventional pain procedures.Interv Pain Med. 2022 Jul 11;1(3):100121. doi: 10.1016/j.inpm.2022.100121. eCollection 2022 Sep. Interv Pain Med. 2022. PMID: 39238521 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alcock E, Regaard A, Browne J. Facet joint injection: a rare form cause of epidural abscess formation. Pain. 2003;103:209–210. - PubMed
-
- Cook NJ, Hanrahan P, Song S. Paraspinal abscess following facet joint injection. Clin Rheumatol. 1999;18:52–53. - PubMed
-
- Ergan M, Macro M, Benhamou CL, Vandermarcq P, Colin T, L'Hirondel JL, et al. Septic arthritis of lumbar facet joints. A review of six cases. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1997;64:386–395. - PubMed
-
- Magee M, Kannangara S, Dennien B, Lonergan R, Emmett L, Van der Wall H. Paraspinal abscess complicating facet joint injection. Clin Nucl Med. 2000;25:71–73. - PubMed
-
- Okazaki K, Sasaki K, Matsuda S, Yuge I, Omiya K, Kido H, et al. Pyogenic arthritis of a lumbar facet joint. Am J Orthop. 2000;29:222–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

