Bioconjugated nanoparticle detection of respiratory syncytial virus infection
- PMID: 17722519
- PMCID: PMC2673827
- DOI: 10.2147/nano.2007.2.1.117
Bioconjugated nanoparticle detection of respiratory syncytial virus infection
Abstract
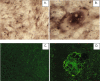
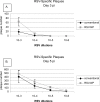
The integration of nanotechnology with biology has produced major advances in molecular diagnostics, therapeutics, and bioengineering. Recent advances have led to the development of functionalized nanoparticles (NPs) that are covalently linked to biological molecules such as antibodies, peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids. These functionalized NPs allow for development of novel diagnostic tools and methods, particularly for pathogens, as rapid and sensitive diagnostics are essential for defining the emergence of infection, determining the period that preventive measures should be applied, for evaluating drug and vaccine efficacy, and for controlling epidemics. In this study, we show that functionalized NPs conjugated to monoclonal antibodies can be used to rapidly and specifically detect respiratory syncytial virus in vitro and in vivo. These results suggest that functionalized NPs can provide direct, rapid, and sensitive detection of viruses and thereby bridge the gap between current cumbersome virus detection assays and the burgeoning need for more rapid and sensitive detection of viral agents.
Figures


References
-
- Agrawal A, Zhang C, Byassee T, et al. Counting single native biomolecules and intact viruses with color-coded nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2006;78:1061–70. - PubMed
-
- Alivisatos AP, Gu W, Larabell Cl. Quantum dots as cellular probes. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2005;7:55–76. - PubMed
-
- Bader MS, McKinsey DS. Viral infections in the elderly. The challenges of managing herpes zoster, influenza, and RSV. Postgrad Med. 2005;118:45–8. 51–4. - PubMed
-
- Bentzen E, House F, Utley TJ, et al. Progression of respiratory syncytial virus infection monitored by fluorescent quantum dot probes. Nano Lett. 2005;5:591–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

