Inferring function using patterns of native disorder in proteins
- PMID: 17722973
- PMCID: PMC1950950
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030162
Inferring function using patterns of native disorder in proteins
Abstract
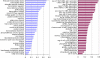
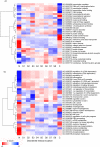
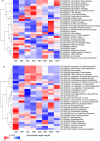
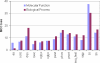
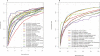
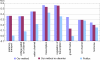
Natively unstructured regions are a common feature of eukaryotic proteomes. Between 30% and 60% of proteins are predicted to contain long stretches of disordered residues, and not only have many of these regions been confirmed experimentally, but they have also been found to be essential for protein function. In this study, we directly address the potential contribution of protein disorder in predicting protein function using standard Gene Ontology (GO) categories. Initially we analyse the occurrence of protein disorder in the human proteome and report ontology categories that are enriched in disordered proteins. Pattern analysis of the distributions of disordered regions in human sequences demonstrated that the functions of intrinsically disordered proteins are both length- and position-dependent. These dependencies were then encoded in feature vectors to quantify the contribution of disorder in human protein function prediction using Support Vector Machine classifiers. The prediction accuracies of 26 GO categories relating to signalling and molecular recognition are improved using the disorder features. The most significant improvements were observed for kinase, phosphorylation, growth factor, and helicase categories. Furthermore, we provide predicted GO term assignments using these classifiers for a set of unannotated and orphan human proteins. In this study, the importance of capturing protein disorder information and its value in function prediction is demonstrated. The GO category classifiers generated can be used to provide more reliable predictions and further insights into the behaviour of orphan and unannotated proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Friedberg I. Automated protein function prediction—The genomic challenge. Brief Bioinform. 2006;7:225–242. - PubMed
-
- Ofran Y, Punta M, Schneider R, Rost B. Beyond annotation transfer by homology novel protein-function prediction methods to assist drug discovery. Drug Discov Today. 2005;10:1475–1482. - PubMed
-
- Jensen LJ, Gupta R, Staerfeldt HH, Brunak S. Prediction of human protein function according to Gene Ontology categories. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:635–642. - PubMed
-
- Jensen LJ, Gupta R, Blom N, Devos D, Tamames J, et al. Prediction of human protein function from post-translational modifications and localization features. J Mol Biol. 2002;319:1257–1265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

