Relationship between phosphorylated histone H2AX formation and cell survival in human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC) as a function of ionizing radiation exposure in the presence or absence of thiol-containing drugs
- PMID: 17723002
- PMCID: PMC1958995
- DOI: 10.1667/RR0975.1
Relationship between phosphorylated histone H2AX formation and cell survival in human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC) as a function of ionizing radiation exposure in the presence or absence of thiol-containing drugs
Abstract
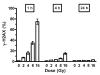
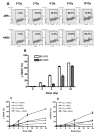
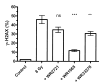
Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC) were exposed to ionizing radiation at doses ranging from 0 to 16 Gy in either the presence or absence of the active thiol forms of amifostine (WR1065), phosphonol (WR255591), N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC), captopril or mesna. Each of these clinically relevant thiols, administered to HMEC at a dose of 4 mM for 30 min prior to irradiation, is known to exhibit antioxidant properties. The purpose of this investigation was to determine the relationship(s), if any, between the frequency of radiation-induced histone H2AX phosphorylation at serine 139 (gamma-H2AX) in cells and subsequent survival, as assessed by colony-forming ability, in exposed cell populations as a function of the presence or absence of each of the five thiol compounds during irradiation. gamma-H2AX formation in irradiated cells, as a function of relative DNA content, was quantified by bivariant flow cytometry analysis with FITC-conjugated gamma-H2AX antibody and nuclear DAPI staining. gamma-H2AX formation in cells was measured as the relative fold increase as a function of the treatment conditions. The frequency of gamma-H2AX-positive cells increased with increasing dose of radiation followed by a dose- and time-dependent decay. The most robust response for gamma-H2AX formation occurred 1 h after irradiation with their relative frequencies decreasing as a function of time 4 and 24 h later. To assess the effects of the various thiols on gamma-H2AX formation, all measurements were made 1 h after irradiation. WR1065 was not only effective in protecting HMEC against gamma-H2AX formation across the entire dose range of radiation exposures used, but it was also significantly more cytoprotective than either its prodrug (WR2721) or disulfide (WR33278) analogue. WR1065 had no significant effect on gamma-H2AX formation when administered immediately or up to 30 min after radiation exposure. An inhibitory effect against gamma-H2AX formation induced by 8 Gy of radiation was expressed by each of the thiols tested. NAC, captopril and mesna were equally effective in reducing the frequency of gamma-H2AX formation, with both WR1065 and WR255591 exhibiting a slightly more robust protective effect. Each of the five thiols was effective in reducing the frequency of gamma-H2AX-positive cells across all phases of the cell cycle. In contrast to the relative ability of each of these thiols to inhibit gamma-H2AX formation after irradiation, NAC, captopril and mesna afforded no protection to HMEC as determined using a colony-forming survival assay. Only WR1065 and WR255591 were effective in reducing the frequencies of radiation-induced gamma-H2AX-positive cells as well as protecting against cell death. These results suggest that the use of gamma-H2AX as a biomarker for screening the efficacy of novel antioxidant radioprotective compounds is highly problematic since their formation and disappearance may be linked to processes beyond simply the formation and repair of radiation-induced DSBs.
Figures


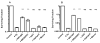
Similar articles
-
Maintenance of manganese superoxide dismutase (SOD2)-mediated delayed radioprotection induced by repeated administration of the free thiol form of amifostine.Radiat Res. 2008 May;169(5):495-505. doi: 10.1667/RR1194.1. Radiat Res. 2008. PMID: 18439041 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin exhibits radiation countermeasures efficacy when used alone or in combination with sulfhydryl containing drugs.Radiat Res. 2014 May;181(5):464-70. doi: 10.1667/RR13672.1. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 24754562 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of amifostine and ionizing radiation on transcriptional patterns of apoptotic genes expressed in human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC).Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Oct 1;60(2):553-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.04.060. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 15380592
-
Gamma histone 2AX (γ-H2AX)as a predictive tool in radiation oncology.Biomarkers. 2014 May;19(3):167-80. doi: 10.3109/1354750X.2014.898099. Epub 2014 Mar 10. Biomarkers. 2014. PMID: 24611829 Review.
-
Evaluation of chemical phototoxicity, focusing on phosphorylated histone H2AX.J Radiat Res. 2015 Mar;56(2):220-8. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rru105. Epub 2014 Dec 4. J Radiat Res. 2015. PMID: 25480829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
WR1065 conjugated to thiol-PEG polymers as novel anticancer prodrugs: broad spectrum efficacy, synergism, and drug resistance reversal.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 28;13:1212604. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1212604. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37576902 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-H2AX in recognition and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks in the context of chromatin.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Oct;36(17):5678-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn550. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18772227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amifostine alleviates radiation-induced lethal small bowel damage via promotion of 14-3-3σ-mediated nuclear p53 accumulation.Oncotarget. 2014 Oct 30;5(20):9756-69. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2386. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25230151 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the efficacy of radiation-modifying compounds using γH2AX as a molecular marker of DNA double-strand breaks.Genome Integr. 2011 Jan 25;2(1):3. doi: 10.1186/2041-9414-2-3. Genome Integr. 2011. PMID: 21261999 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Influence of the ATM Protein in the Treatment of Human Cells with Different Radioprotective Drugs: Comparisons between Antioxidative and Pro-Episkevic Strategies.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 13;13(3):524. doi: 10.3390/biom13030524. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahashi A, Ohnishi T. Does γH2AX foci formation depend on the presence of DNA double strand breaks? Cancer Lett. 2005;229:171–179. - PubMed
-
- Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS, Bonner WM. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:5858–5868. - PubMed
-
- Stiff T, O’Driscoll M, Rief N, Iwabuchi K, Lobrich M, Jeggo PA. ATM and DNA-PK function redundantly to phosphorylate H2AX after exposure to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2390–2396. - PubMed
-
- Paull TT, Rogakou EP, Yamazaki V, Kirchgessner CU, Gellert M, Bonner WM. A critical role for histone H2AX in recruitment of repair factors to nuclear foci after DNA damage. Curr Biol. 2000;10:886–895. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

