High-efficiency protein expression in plants from agroinfection-compatible Tobacco mosaic virus expression vectors
- PMID: 17723150
- PMCID: PMC2014746
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-7-52
High-efficiency protein expression in plants from agroinfection-compatible Tobacco mosaic virus expression vectors
Abstract
Background: Plants are increasingly being examined as alternative recombinant protein expression systems. Recombinant protein expression levels in plants from Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)-based vectors are much higher than those possible from plant promoters. However the common TMV expression vectors are costly, and at times technically challenging, to work with. Therefore it was a goal to develop TMV expression vectors that express high levels of recombinant protein and are easier, more reliable, and more cost-effective to use.
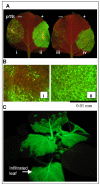
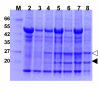
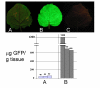
Results: We have constructed a Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter-driven TMV expression vector that can be delivered as a T-DNA to plant cells by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Co-introduction (by agroinfiltration) of this T-DNA along with a 35S promoter driven gene for the RNA silencing suppressor P19, from Tomato bushy stunt virus (TBSV) resulted in essentially complete infection of the infiltrated plant tissue with the TMV vector by 4 days post infiltration (DPI). The TMV vector produced between 600 and 1200 micrograms of recombinant protein per gram of infiltrated tissue by 6 DPI. Similar levels of recombinant protein were detected in systemically infected plant tissue 10-14 DPI. These expression levels were 10 to 25 times higher than the most efficient 35S promoter driven transient expression systems described to date.
Conclusion: These modifications to the TMV-based expression vector system have made TMV vectors an easier, more reliable and more cost-effective way to produce recombinant proteins in plants. These improvements should facilitate the production of recombinant proteins in plants for both research and product development purposes. The vector should be especially useful in high-throughput experiments.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TRBO: a high-efficiency tobacco mosaic virus RNA-based overexpression vector.Plant Physiol. 2007 Dec;145(4):1232-40. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.106377. Epub 2007 Aug 24. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17720752 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of the selectable marker gene from transgenic tobacco plants by expression of Cre recombinase from a tobacco mosaic virus vector through agroinfection.Transgenic Res. 2006 Jun;15(3):375-84. doi: 10.1007/s11248-006-0011-6. Transgenic Res. 2006. PMID: 16779652
-
Assessment of the effectiveness of a nuclear-launched TMV-based replicon as a tool for foreign gene expression in plants in comparison to direct gene expression from a nuclear promoter.Transgenic Res. 2006 Feb;15(1):107-13. doi: 10.1007/s11248-005-2942-8. Transgenic Res. 2006. PMID: 16475015
-
Historical overview of research on the tobacco mosaic virus genome: genome organization, infectivity and gene manipulation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999 Mar 29;354(1383):569-82. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0408. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999. PMID: 10212936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tobacco mosaic virus and the virescence of biotechnology.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999 Mar 29;354(1383):665-73. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0419. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999. PMID: 10212947 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Narcissus mosaic viral vector system for protein expression and flavonoid production.Plant Methods. 2013 Jul 13;9(1):28. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-9-28. Plant Methods. 2013. PMID: 23849589 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of the GDP-L-galactose phosphorylase gene family in bread wheat.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Nov 26;19(1):515. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2123-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31771507 Free PMC article.
-
An N-terminal motif in NLR immune receptors is functionally conserved across distantly related plant species.Elife. 2019 Nov 27;8:e49956. doi: 10.7554/eLife.49956. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31774397 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced foreign protein accumulation in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves co-infiltrated with a TMV vector and plant cell cycle regulator genes.Transgenic Res. 2019 Aug;28(3-4):411-417. doi: 10.1007/s11248-019-00128-3. Epub 2019 May 16. Transgenic Res. 2019. PMID: 31098823
-
An efficient Foxtail mosaic virus vector system with reduced environmental risk.BMC Biotechnol. 2010 Dec 16;10:88. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-10-88. BMC Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 21162736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scholthof KB, Mirkov TE, Scholthof HB. Plant virus gene vectors: biotechnology applications in agriculture and medicine. Genet Eng (NY) 2002;24:67–85. - PubMed
-
- Yusibov V, Shivprasad S, Turpen TH, Dawson W, Koprowski H. Plant viral vectors based on tobamoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1999;240:81–94. - PubMed
-
- Pogue GP, Lindbo JA, Dawson WO, Turpen TH, (eds) Tobamovirus transient expression vectors: Tools for plant biology and high-level expression of foreign proteins in plants. In: Gelvin SB, Schilperoot RA, editor. Plant Molecular Biology Manual. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1998.
-
- Breiteneder H, Krebitz M, Wiedermann U, Wagner B, Essl D, Steinkellner H, Turpen TH, Ebner C, Buck D, Niggemann B, et al. Rapid production of recombinant allergens in Nicotiana benthamiana and their impact on diagnosis and therapy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001;124:48–50. doi: 10.1159/000053665. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

