Protein kinase C zeta. A novel regulator of both phosphorylation and de-phosphorylation of cardiac sarcomeric proteins
- PMID: 17724026
- PMCID: PMC2597085
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M703670200
Protein kinase C zeta. A novel regulator of both phosphorylation and de-phosphorylation of cardiac sarcomeric proteins
Abstract
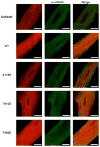
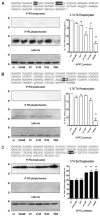
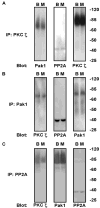
Our experiments investigated associations of specific isoforms of protein kinase C (PKC) with individual proteins in the cardiac troponin complex. Troponin I (cTnI) associated with PKCepsilon and zeta and troponin T (cTnT) associated with PKC alpha, delta, and epsilon. Based on its association with cTnI, we hypothesized that PKCzeta is a major regulator of myofilament protein phosphorylation. To test this, we infected adult cardiac myocytes with adenoviral constructs containing DsRed monomer-tagged wild type (WT) and the following constitutively active forms of PKCzeta: the pseudo-substrate region (A119E), 3'-phospho-inositide-dependent kinase-1 (T410E), and auto-phosphorylation (T560E). The A119E and T410E mutants displayed increased localization to the Z-discs compared with WT and T560E. Immunoprecipitations were performed in myocytes expressing PKCzeta using PKC phospho-motif antibodies to determine the phosphorylation of cTnI, cTnT, tropomyosin, myosin-binding protein C, and desmin. We did not find serine (Ser) phosphorylation of cTnI or cTnT. However, we observed a significant decrease in threonine (Thr) phosphorylation of cTnI and cTnT notably by PKCzeta T560E. Ser phosphorylation of tropomyosin was increased by all three active mutants of PKCzeta. Ser/Thr phosphorylation of myosin-binding protein C increased primarily by PKCzeta A119E. Both PKCzeta A119E and T410E mutants increased desmin Ser/Thr phosphorylation. To explain the apparent Thr dephosphorylation of cTnI and cTnT, we hypothesized that PKCzeta exists as a complex with p21-activated kinase-1 (Pak1) and protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), and this was confirmed by immunoprecipitation Western blot. Our data demonstrate that PKCzeta is a novel regulator of myofilament protein phosphorylation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Distinct sarcomeric substrates are responsible for protein kinase D-mediated regulation of cardiac myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity and cross-bridge cycling.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 19;285(8):5674-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.066456. Epub 2009 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20018870 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin and PIP3 activate PKC-zeta by mechanisms that are both dependent and independent of phosphorylation of activation loop (T410) and autophosphorylation (T560) sites.Biochemistry. 2001 Jan 9;40(1):249-55. doi: 10.1021/bi0018234. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11141077
-
Intracellular localization and functional effects of P21-activated kinase-1 (Pak1) in cardiac myocytes.Circ Res. 2004 Feb 6;94(2):194-200. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000111522.02730.56. Epub 2003 Dec 11. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 14670848
-
Posttranslational modifications of cardiac troponin T: an overview.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 Oct;63:47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Jul 18. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23871791 Review.
-
PRKCE gene encoding protein kinase C-epsilon-Dual roles at sarcomeres and mitochondria in cardiomyocytes.Gene. 2016 Sep 15;590(1):90-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.06.016. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Gene. 2016. PMID: 27312950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
APPL1 mediates adiponectin-induced LKB1 cytosolic localization through the PP2A-PKCzeta signaling pathway.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Oct;25(10):1773-85. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-0082. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21835890 Free PMC article.
-
Redox signaling and cardiac sarcomeres.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 25;286(12):9921-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R110.175489. Epub 2011 Jan 21. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21257753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinase C (PKC)ζ-mediated Gαq stimulation of ERK5 protein pathway in cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 2;287(10):7792-802. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.282210. Epub 2012 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22232556 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of tropomyosin extends cooperative binding of myosin beyond a single regulatory unit.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009 Jan;66(1):10-23. doi: 10.1002/cm.20321. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009. PMID: 18985725 Free PMC article.
-
The BMI1 polycomb protein represses cyclin G2-induced autophagy to support proliferation in chronic myeloid leukemia cells.Leukemia. 2015 Oct;29(10):1993-2002. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.112. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Leukemia. 2015. PMID: 25925206
References
-
- Solaro RJ. Handbook of Physiology. Oxford University Press; New York, NY: 2001. pp. 264–300.
-
- Solaro RJ, Montgomery DM, Wang L, Burkart EM, Ke Y, Vahebi S, Buttrick P. J Nucl Cardiol. 2002;9:523–533. - PubMed
-
- Newton AC. Chem Rev. 2001;101:2353–2364. - PubMed
-
- Goldspink PH, Montgomery DE, Walker LA, Urboniene D, McKinney RD, Geenen DL, Solaro RJ, Buttrick PM. Circ Res. 2004;95:424–432. - PubMed
-
- Huang L, Wolska BM, Montgomery DE, Burkart EM, Buttrick PM, Solaro RJ. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;280:C1114–C1120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

