Helicobacter pylori induces CCL20 expression
- PMID: 17724069
- PMCID: PMC2168315
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00731-07
Helicobacter pylori induces CCL20 expression
Retraction in
-
Retraction. Helicobacter pylori induces CCL20 expression.Infect Immun. 2011 Jan;79(1):545. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01068-10. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21177934 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
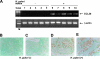
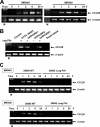
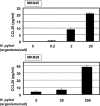
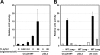
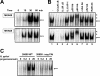
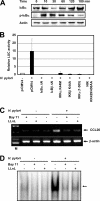
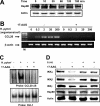
CCL20 attracts immature dendritic cells and memory T cells and plays a role on mucosal surfaces in inflammation. However, whether Helicobacter pylori infection induces CCL20 in human gastric epithelial cells remains to be determined. The aim of this study was to analyze the molecular mechanism of H. pylori-induced CCL20 expression. Expression of CCL20 mRNA was assessed by reverse transcription-PCR. Five normal and five H. pylori-infected gastric tissue samples were stained immunohistochemically for CCL20. A luciferase assay was used to monitor activation of the CCL20 gene promoter, and an electrophoretic mobility shift assay was used to explore the binding of transcription factors to this promoter. The CCL20 expression in epithelial cells of H. pylori-positive tissues was higher than that in H. pylori-negative tissues. H. pylori induced CCL20 expression in gastric epithelial cell lines, and the induction was dependent on an intact cag pathogenicity island. Activation of the CCL20 promoter by H. pylori occurred through the action of NF-kappaB. Transfection of IkappaB kinase and NF-kappaB-inducing kinase dominant negative mutants inhibited H. pylori-mediated activation of CCL20. Treatment with an inhibitor of Hsp90 suppressed H. pylori-induced CCL20 mRNA due to deactivation of NF-kappaB. Collectively, these results suggest that H. pylori activates NF-kappaB through an intracellular signaling pathway that involves IkappaB kinase and NF-kappaB-inducing kinase, leading to CCL20 gene transcription, and that Hsp90 is a crucial regulator of H. pylori-induced CCL20 expression, presumably contributing to the immune response in H. pylori.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 through activation of nuclear factor kappaB.Gastroenterology. 2003 Apr;124(4):983-92. doi: 10.1053/gast.2003.50152. Gastroenterology. 2003. PMID: 12671895
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of capsaicin in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells.Helicobacter. 2007 Oct;12(5):510-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2007.00521.x. Helicobacter. 2007. PMID: 17760719
-
Helicobacter pylori in a Korean isolate activates mitogen-activated protein kinases, AP-1, and NF-kappaB and induces chemokine expression in gastric epithelial AGS cells.Lab Invest. 2004 Jan;84(1):49-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.labinvest.3700010. Lab Invest. 2004. PMID: 14631383
-
Host cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection.Int J Med Microbiol. 2001 Sep;291(4):299-305. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00133. Int J Med Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11680790 Review.
-
Chemokine expression in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa.J Gastroenterol. 1998 Oct;33(5):613-7. doi: 10.1007/s005350050146. J Gastroenterol. 1998. PMID: 9773923 Review.
Cited by
-
Interplay between Helicobacter pylori and immune cells in immune pathogenesis of gastric inflammation and mucosal pathology.Cell Mol Immunol. 2010 Jul;7(4):255-9. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2010.2. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20190789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate immune responses of pulmonary epithelial cells to Burkholderia pseudomallei infection.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 6;4(10):e7308. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007308. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19806192 Free PMC article.
-
CCL20 is overexpressed in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected monocytes and inhibits the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Nov;162(2):289-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04168.x. Epub 2010 Sep 1. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20819093 Free PMC article.
-
Functional relevance of novel p300-mediated lysine 314 and 315 acetylation of RelA/p65.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Mar;36(5):1665-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn003. Epub 2008 Feb 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18263619 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced expression of CXCL13 in human Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis.Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Oct;56(10):2887-94. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1717-8. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21647655
References
-
- Baggiolini, M., and P. Loetscher. 2000. Chemokines in inflammation and immunity. Immunol. Today 21:418-420. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau, J., and R. M. Steinman. 1998. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392:245-252. - PubMed
-
- Blaser, M. J., G. I. Perez-Perez, H. Kleanthous, T. L. Cover, R. M. Peek, P. H. Chyou, G. N. Stemmermann, and A. Nomura. 1995. Infection with Helicobacter pylori strains possessing cagA is associated with an increased risk of developing adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Cancer Res. 55:2111-2115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

