In vitro activity of human beta-defensin 2 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the presence of tear fluid
- PMID: 17724155
- PMCID: PMC2151451
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01317-06
In vitro activity of human beta-defensin 2 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the presence of tear fluid
Abstract
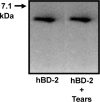
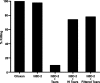
Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes vision-threatening keratitis and is difficult to treat due to emerging resistance. Human beta-defensin 2 (hBD-2) is an antimicrobial peptide expressed by ocular surface epithelia with broad-spectrum activity against various pathogens, including P. aeruginosa. The activity of hBD-2 against P. aeruginosa in the presence of human tears or NaCl was studied. In some experiments, tears were heat-inactivated, filtered, and separated into cationic/anionic fractions or mucin MUC5AC was removed by immunoprecipitation before use. Immunoprecipitation was performed to study the interaction between hBD-2 and MUC5AC. hBD-2 activity was reduced by 40 to 90% in the presence of 17.5 to 70% (vol/vol) tears. NaCl reduced hBD-2 activity, but at most it could account for only 36% of the inhibitory effect of tears. Heat inactivation and filtration attenuated the ability of tears to inhibit hBD-2 activity by 65 and 68%, respectively. Anionic tear fractions significantly reduced (86%) the activity of hBD-2, whereas only a 22% reduction was observed with the cationic fractions. In the absence of MUC5AC, the activity of hBD-2 was restored by 64%. Immunoprecipitation studies suggested that the loss of hBD-2 activity in tears is due to a direct binding interaction with MUC5AC. Our data showed that the antimicrobial activity of hBD-2 is sensitive to the presence of human tears and that this is partly due to the salt content and also the presence of MUC5AC. These data cast doubt on the effectiveness of hBD-2 as an antimicrobial peptide, and additional studies are required to conclusively elucidate its role in innate immunity at the ocular surface in vivo.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of preservative-free artificial tears on the antimicrobial activity of human beta-defensin-2 and cathelicidin LL-37 in vitro.Eye Contact Lens. 2005 Jan;31(1):34-8. doi: 10.1097/01.icl.0000146320.64438.8c. Eye Contact Lens. 2005. PMID: 15665670 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular surface expression and in vitro activity of antimicrobial peptides.Curr Eye Res. 2007 Jul-Aug;32(7-8):595-609. doi: 10.1080/02713680701446653. Curr Eye Res. 2007. PMID: 17852183 Free PMC article.
-
Two arginine residues in the COOH-terminal of human β-defensin-3 constitute an essential motif for antimicrobial activity and IL-6 production.Exp Dermatol. 2017 Nov;26(11):1026-1032. doi: 10.1111/exd.13361. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Exp Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28418601
-
Human defensins.J Mol Med (Berl). 2005 Aug;83(8):587-95. doi: 10.1007/s00109-005-0657-1. Epub 2005 Apr 9. J Mol Med (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15821901 Review.
-
Modulation of Human β-Defensin-1 Production by Viruses.Viruses. 2017 Jun 21;9(6):153. doi: 10.3390/v9060153. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28635669 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AMPed up immunity: how antimicrobial peptides have multiple roles in immune defense.Trends Immunol. 2009 Mar;30(3):131-41. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2008.12.003. Epub 2009 Feb 13. Trends Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19217824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parasiticidal activity of human alpha-defensin-5 against Toxoplasma gondii.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2010 Jun;46(6):560-5. doi: 10.1007/s11626-009-9271-9. Epub 2010 Feb 5. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2010. PMID: 20135360
-
Mammals' humoral immune proteins and peptides targeting the bacterial envelope: from natural protection to therapeutic applications against multidrug-resistant Gram-negatives.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022 Jun;97(3):1005-1037. doi: 10.1111/brv.12830. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022. PMID: 35043558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BD-2 and BD-3 increase skin flap survival in a model of ischemia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection.Sci Rep. 2019 May 27;9(1):7854. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44153-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31133641 Free PMC article.
-
The role of antimicrobial peptides at the ocular surface.Ophthalmic Res. 2009;41(2):60-75. doi: 10.1159/000187622. Epub 2008 Dec 20. Ophthalmic Res. 2009. PMID: 19122467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aarbiou, J., R. M. Verhoosel, S. Van Wetering, W. I. De Boer, J. H. Van Krieken, S. V. Litvinov, K. F. Rabe, and P. S. Hiemstra. 2004. Neutrophil defensins enhance lung epithelial wound closure and mucin gene expression in vitro. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 30:193-201. - PubMed
-
- Ahn, C. S., T. McMahon, J. Sugar, L. Zhou, and B. Y. Yue. 1999. Levels of alpha1-proteinase inhibitor and alpha2-macroglobulin in the tear film of patients with keratoconus. Cornea 18:194-198. - PubMed
-
- Akinbi, H. T., V. Narendran, A. K. Pass, P. Markart, and S. B. Hoath. 2004. Host defense proteins in vernix caseosa and amniotic fluid. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 191:2090-2096. - PubMed
-
- Befus, A. D., C. Mowat, M. Gilchrist, J. Hu, S. Solomon, and A. Bateman. 1999. Neutrophil defensins induce histamine secretion from mast cells: mechanisms of action. J. Immunol. 163:947-953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

