Power analysis for genome-wide association studies
- PMID: 17725844
- PMCID: PMC2042984
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-8-58
Power analysis for genome-wide association studies
Abstract
Background: Genome-wide association studies are a promising new tool for deciphering the genetics of complex diseases. To choose the proper sample size and genotyping platform for such studies, power calculations that take into account genetic model, tag SNP selection, and the population of interest are required.
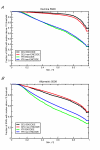
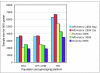
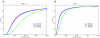
Results: The power of genome-wide association studies can be computed using a set of tag SNPs and a large number of genotyped SNPs in a representative population, such as available through the HapMap project. As expected, power increases with increasing sample size and effect size. Power also depends on the tag SNPs selected. In some cases, more power is obtained by genotyping more individuals at fewer SNPs than fewer individuals at more SNPs.
Conclusion: Genome-wide association studies should be designed thoughtfully, with the choice of genotyping platform and sample size being determined from careful power calculations.
Figures


References
-
- Matsuzaki H, Dong S, Loi H, Di X, Liu G, Hubbell E, Law J, Berntsen T, Chadha M, Hui H, Yang G, Kennedy GC, Webster TA, Cawley S, Walsh PS, Jones KW, Fodor SPA, Mei R. Genotyping over 100,000 SNPs on a pair of oligonucleotide arrays. Nat Methods. 2004;1:109–111. doi: 10.1038/nmeth718. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

