Widespread endocrine disruption and reproductive impairment in an estuarine fish population exposed to seasonal hypoxia
- PMID: 17725976
- PMCID: PMC2279220
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2007.0921
Widespread endocrine disruption and reproductive impairment in an estuarine fish population exposed to seasonal hypoxia
Abstract
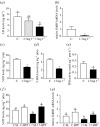
The long-term effects on marine fish populations of the recent increase worldwide in the incidence of coastal hypoxia are unknown. Here we show that chronic environmental exposure of Atlantic croaker (Micropogonias undulatus) to hypoxia in a Florida estuary caused marked suppression of ovarian and testicular growth which was accompanied by endocrine disruption. Laboratory hypoxia studies showed that the endocrine disruption was associated with impairment of reproductive neuroendocrine function and decreases in hypothalamic serotonin (5-HT) content and the activity of the 5-HT biosynthetic enzyme, tryptophan hydroxylase. Pharmacological restoration of hypothalamic 5-HT levels also restored neuroendocrine function, indicating that the stimulatory serotonergic neuroendocrine pathway is a major site of hypoxia-induced inhibition. Inhibition of tryptophan hydroxylase activity to downregulate reproductive activity could have evolved as an adaptive mechanism to survive periodic hypoxia, but in view of the recent increased incidence of coastal hypoxia could become maladaptive and potentially affect fish population abundance and threaten valuable fishery resources.
Figures





References
-
- Allen Y, Scott A.P, Matthiessen P, Haworth S, Thain J.E, Feist S. Survey of estrogenic activity in United Kingdom estuarine and coastal waters and its effects on gonadal development of the flounder Platichthys flesus. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999;18:1791–1800. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1999)018<1791:SOEAIU>2.3.CO;2 - DOI
-
- Bell G.W, Eggleston D.B. Species-specific avoidance responses by blue crabs and fish to chronic and episodic hypoxia. Mar. Biol. 2005;146:761–770. doi:10.1007/s00227-005-1614-9 - DOI
-
- Billard R, Bry C, Gillet C. Stress, environment and reproduction in teleost fish. In: Pickering A.D, editor. Stress and fish. Academic Press; London, UK: 1981. pp. 185–208.
-
- Brown R.M, Kehr W, Carlsson A. Functional and biochemical aspects of catecholamine metabolism in brain under hypoxia. Brain Res. 1975;85:491–509. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(75)90822-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brown-Peterson N, Thomas P, Arnold C.R. Reproductive biology of the spotted seatrout, Cynoscion nebulosus, in south Texas. Fish. Bull. 1988;86:373–388.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
