A rapid high-throughput method for the detection and quantification of RNA editing based on high-resolution melting of amplicons
- PMID: 17726051
- PMCID: PMC2034463
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm640
A rapid high-throughput method for the detection and quantification of RNA editing based on high-resolution melting of amplicons
Abstract
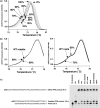
We describe a rapid, high-throughput method to scan for new RNA editing sites. This method is adapted from high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis of amplicons, a technique used in clinical research to detect mutations in genomes. The assay was validated by the discovery of six new editing sites in different chloroplast transcripts of Arabidopsis thaliana. A screen of a collection of mutants uncovered a mutant defective for editing of one of the newly discovered sites. We successfully adapted the technique to quantify editing of partially edited sites in different individuals or different tissues. This new method will be easily applicable to RNA from any organism and should greatly accelerate the study of the role of RNA editing in physiological processes as diverse as plant development or human health.
Figures


References
-
- Gott JM, Emeson RB. Functions and mechanisms of RNA editing. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2000;34:499–531. - PubMed
-
- Young SG. Recent progress in understanding apolipoprotein B. Circulation. 1990;82:1574–1594. - PubMed
-
- Burns CM, Chu H, Rueter SM, Hutchinson LK, Canton H, Sanders-Bush E, Emeson RB. Regulation of serotonin-2C receptor G-protein coupling by RNA editing. Nature. 1997;387:303–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

