Cdc42 acts downstream of Bazooka to regulate neuroblast polarity through Par-6 aPKC
- PMID: 17726059
- PMCID: PMC1988841
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.014902
Cdc42 acts downstream of Bazooka to regulate neuroblast polarity through Par-6 aPKC
Abstract
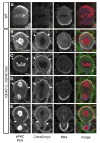
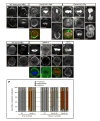
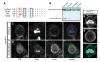
Cdc42 recruits Par-6-aPKC to establish cell polarity from worms to mammals. Although Cdc42 is reported to have no function in Drosophila neuroblasts, a model for cell polarity and asymmetric cell division, we show that Cdc42 colocalizes with Par-6-aPKC at the apical cortex in a Bazooka-dependent manner, and is required for Par-6-aPKC localization. Loss of Cdc42 disrupts neuroblast polarity: cdc42 mutant neuroblasts have cytoplasmic Par-6-aPKC, and this phenotype is mimicked by neuroblast-specific expression of a dominant-negative Cdc42 protein or a Par-6 protein that lacks Cdc42-binding ability. Conversely, expression of constitutively active Cdc42 leads to ectopic Par-6-aPKC localization and corresponding cell polarity defects. Bazooka remains apically enriched in cdc42 mutants. Robust Cdc42 localization requires Par-6, indicating the presence of feedback in this pathway. In addition to regulating Par-6-aPKC localization, Cdc42 increases aPKC activity by relieving Par-6 inhibition. We conclude that Cdc42 regulates aPKC localization and activity downstream of Bazooka, thereby directing neuroblast cell polarity and asymmetric cell division.
Figures

References
-
- Albertson R, Doe CQ. Dlg, Scrib and Lgl regulate neuroblast cell size and mitotic spindle asymmetry. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:166–70. - PubMed
-
- Barros CS, Phelps CB, Brand AH. Drosophila nonmuscle myosin II promotes the asymmetric segregation of cell fate determinants by cortical exclusion rather than active transport. Dev Cell. 2003;5:829–40. - PubMed
-
- Beers M, Kemphues K. Depletion of the co-chaperone CDC-37 reveals two modes of PAR-6 cortical association in C. elegans embryos. Development. 2006;133:3745–54. - PubMed
-
- Betschinger J, Mechtler K, Knoblich JA. The Par complex directs asymmetric cell division by phosphorylating the cytoskeletal protein Lgl. Nature. 2003;422:326–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

