Breaking up the correlation between efficacy and toxicity for nonviral gene delivery
- PMID: 17726101
- PMCID: PMC1964826
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0703882104
Breaking up the correlation between efficacy and toxicity for nonviral gene delivery
Abstract
Nonviral nucleic acid delivery to cells and tissues is considered a standard tool in life science research. However, although an ideal delivery system should have high efficacy and minimal toxicity, existing materials fall short, most of them being either too toxic or little effective. We hypothesized that disulfide cross-linked low-molecular-weight (MW) linear poly(ethylene imine) (MW<4.6 kDa) would overcome this limitation. Investigations with these materials revealed that the extracellular high MW provided outstandingly high transfection efficacies (up to 69.62+/-4.18% in HEK cells). We confirmed that the intracellular reductive degradation produced mainly nontoxic fragments (cell survival 98.69+/-4.79%). When we compared the polymers in >1,400 individual experiments to seven commercial transfection reagents in seven different cell lines, we found highly superior transfection efficacies and substantially lower toxicities. This renders reductive degradation a highly promising tool for the design of new transfection materials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
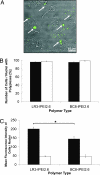
 (P < 0.05) or ★ (P < 0.01).
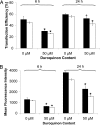
(P < 0.05) or ★ (P < 0.01).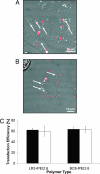
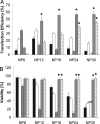
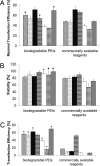
 (P < 0.05) or by ★ (P < 0.01).
(P < 0.05) or by ★ (P < 0.01).References
-
- Lv H, Zhang S, Wang B, Cui S, Yan J. J Control Release. 2006;114:100–109. - PubMed
-
- Wagner E, Kloeckner J. Adv Polym Sci. 2006;192:135–173.
-
- Park TG, Jeong JH, Kim SW. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58:467–486. - PubMed
-
- Hunter AC. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58:1523–1531. - PubMed
-
- Lungwitz U, Breunig M, Blunk T, Gopferich A. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2005;60:247–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

