Lsh controls Hox gene silencing during development
- PMID: 17726103
- PMCID: PMC1955459
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0703669104
Lsh controls Hox gene silencing during development
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 9;104(41):16389
Abstract
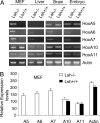
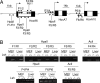
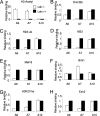
Polycomb-mediated repression and DNA methylation are important epigenetic mechanisms of gene silencing. Recent evidence suggests a functional link between the polycomb repressive complex (PRC) and Dnmts in cancer cells. Here we provide evidence that Lsh, a regulator of DNA methylation, is also involved in normal control of PRC-mediated silencing during embryogenesis. We demonstrate that Lsh, a SNF2 homolog, can associate with some Hox genes and regulates Dnmt3b binding, DNA methylation, and silencing of Hox genes during development. Moreover, Lsh can associate with PRC1 components and influence PRC-mediated histone modifications. Thus Lsh is part of a physiological feedback loop that reinforces DNA methylation and silencing of PRC targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Jones PA. Semin Hematol. 2005;42:S3–8. - PubMed
-
- Goll MG, Bestor TH. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:481–514. - PubMed
-
- Sparmann A, van Lohuizen M. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:846–856. - PubMed
-
- Widschwendter M, Fiegl H, Egle D, Mueller-Holzner E, Spizzo G, Marth C, Weisenberger DJ, Campan M, Young J, Jacobs I, Laird PW. Nat Genet. 2007;39:157–158. - PubMed
-
- Schlesinger Y, Straussman R, Keshet I, Farkash S, Hecht M, Zimmerman J, Eden E, Yakhini Z, Ben-Shushan E, Reubinoff BE, et al. Nat Genet. 2007;39:232–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

