Upregulation of bfl-1 is a potential mechanism of chemoresistance in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
- PMID: 17726463
- PMCID: PMC2360383
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603951
Upregulation of bfl-1 is a potential mechanism of chemoresistance in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Abstract
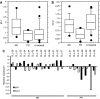
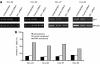
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (B-CLL) is characterised by the progressive accumulation of monoclonal CD5(+) B cells. In a previous study, we have analysed the expression profile of apoptosis-regulating genes using a cDNA-based microarray and found overexpression of the antiapoptotic bcl-2 family member, bfl-1, in B-CLL cells with an apoptosis-resistant phenotype. In this study, bfl-1 mRNA levels have been determined by competitive PCR in an extended population of B-CLL patients to characterise its role in disease progression and development of chemoresistance. bfl-1 levels were significantly higher in patients with no response (NR) to last chemotherapy than in patients responding (partial response (PR)) to last chemotherapy (P<0.05) and in patients who had not required treatment (P<0.05). We found no correlation between bfl-1 mRNA levels and disease progression, IGHV mutational status or other clinical parameters. In addition, bfl-1 mRNA levels were inversely correlated with apoptotic response to in vitro fludarabine treatment of B-CLL cells. Specific downregulation of bfl-1 using siRNA induced apoptosis in resistant cells. Our data suggest that bfl-1 contributes to chemoresistance and might be a therapeutic target in B-CLL.
Figures


References
-
- Aguilar-Santelises M, Rottenberg ME, Lewin N, Mellstedt H, Jondal M (1996) Bcl-2, Bax and p53 expression in B-CLL in relation to in vitro survival and clinical progression. Int J Cancer 69: 114–119 - PubMed
-
- Åleskog A, Tobin G, Laurell A, Thunberg U, Lindhagen E, Roos G, Nilsson K, Nygren P, Sundstrom C, Hoglund M, Larsson R, Rosenquist R (2004) VH gene mutation status and cellular drug resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Eur J Haematol 73: 407–411 - PubMed
-
- Bernal A, Pastore RD, Asgary Z, Keller SA, Cesarman E, Liou HC, Schattner EJ (2001) Survival of leukemic B cells promoted by engagement of the antigen receptor. Blood 98: 3050–3057 - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG, Colman PM, Day CL, Adams JM, Huang DCS (2005) Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell 17: 393–403 - PubMed
-
- Cheson BD, Bennet JM, Grevre M, Kay N, Keating MJ, O'Brien S, Rai KR (1996) National Cancer Institute-sponsored working group guidelines for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: revised guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. Blood 87: 4990–4997 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

