PERK eIF2 alpha kinase is required to regulate the viability of the exocrine pancreas in mice
- PMID: 17727724
- PMCID: PMC2072952
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-8-38
PERK eIF2 alpha kinase is required to regulate the viability of the exocrine pancreas in mice
Abstract
Background: Deficiency of the PERK eIF2 alpha kinase in humans and mice results in postnatal exocrine pancreatic atrophy as well as severe growth and metabolic anomalies in other organs and tissues. To determine if the exocrine pancreatic atrophy is due to a cell-autonomous defect, the Perk gene was specifically ablated in acinar cells of the exocrine pancreas in mice.
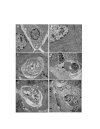
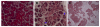
Results: We show that expression of PERK in the acinar cells is required to maintain their viability but is not required for normal protein synthesis and secretion. Exocrine pancreatic atrophy in PERK-deficient mice was previously attributed to uncontrolled ER-stress followed by apoptotic cell death based on studies in cultured fibroblasts. However, we have found no evidence for perturbations in the endoplasmic reticulum or ER-stress and show that acinar cells succumb to a non-apoptotic form of cell death, oncosis, which is associated with a pronounced inflammatory response and induction of the pancreatitis stress response genes. We also show that mice carrying a knockout mutation of PERK's downstream target, ATF4, exhibit pancreatic deficiency caused by developmental defects and that mice ablated for ATF4's transcriptional target CHOP have a normal exocrine pancreas.
Conclusion: We conclude that PERK modulates secretory capacity of the exocrine pancreas by regulating cell viability of acinar cells.
Figures
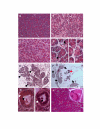
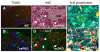
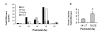
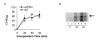

References
-
- Zhang P, McGrath B, Li S, Frank A, Zambito F, Reinert J, Gannon M, Ma K, McNaughton K, Cavener DR. The PERK eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinase is required for the development of the skeletal system, postnatal growth, and the function and viability of the pancreas. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:3864–3874. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.11.3864-3874.2002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

