Isoform-selective susceptibility of DISC1/phosphodiesterase-4 complexes to dissociation by elevated intracellular cAMP levels
- PMID: 17728464
- PMCID: PMC6673124
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1493-07.2007
Isoform-selective susceptibility of DISC1/phosphodiesterase-4 complexes to dissociation by elevated intracellular cAMP levels
Abstract
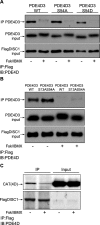
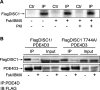
Disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) is a genetic susceptibility factor for schizophrenia and related severe psychiatric conditions. DISC1 is a multifunctional scaffold protein that is able to interact with several proteins, including the independently identified schizophrenia risk factor phosphodiesterase-4B (PDE4B). Here we report that the 100 kDa full-length DISC1 isoform (fl-DISC1) can bind members of each of the four gene, cAMP-specific PDE4 family. Elevation of intracellular cAMP levels, so as to activate protein kinase A, caused the release of PDE4D3 and PDE4C2 isoforms from fl-DISC1 while not affecting binding of PDE4B1 and PDE4A5 isoforms. Using a peptide array strategy, we show that PDE4D3 binds fl-DISC1 through two regions found in common with PDE4B isoforms, the interaction of which is supplemented because of the presence of additional PDE4B-specific binding sites. We propose that the additional binding sites found in PDE4B1 underpin its resistance to release during cAMP elevation. We identify, for the first time, a functional distinction between the 100 kDa long DISC1 isoform and the short 71 kDa isoform. Thus, changes in the expression pattern of DISC1 and PDE4 isoforms offers a means to reprogram their interaction and to determine whether the PDE4 sequestered by DISC1 is released after cAMP elevation. The PDE4B-specific binding sites encompass point mutations in mouse Disc1 that confer phenotypes related to schizophrenia and depression and that affect binding to PDE4B. Thus, genetic variation in DISC1 and PDE4 that influence either isoform expression or docking site functioning may directly affect psychopathology.
Figures





References
-
- Arnsten AF, Ramos BP, Birnbaum SG, Taylor JR. Protein kinase A as a therapeutic target for memory disorders: rationale and challenges. Trends Mol Med. 2005;11:121–128. - PubMed
-
- Baillie GS, Huston E, Scotland G, Hodgkin M, Gall I, Peden AH, MacKenzie C, Houslay ES, Currie R, Pettitt TR, Walmsley AR, Wakelam MJ, Warwicker J, Houslay MD. TAPAS-1, a novel microdomain within the unique N-terminal region of the PDE4A1 cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase that allows rapid, Ca2+-triggered membrane association with selectivity for interaction with phosphatidic acid. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:28298–28309. - PubMed
-
- Baillie GS, Scott JD, Houslay MD. Compartmentalisation of phosphodiesterases and protein kinase A: opposites attract. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:3264–3270. - PubMed
-
- Baillie GS, Adams DR, Bahri N, Houslay TM, Vadrevu S, Meng D, Li X, Dunlop A, Milligan G, Bolger GB, Klussmann E, Houslay MD. Mapping binding sites for the PDE4D5 cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase to the N- and C-domains of betaarrestin using spot-immobilised peptide arrays. Biochem J. 2007;404:71–80. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
