Performance of a pneumolysin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of pneumococcal infections
- PMID: 17728474
- PMCID: PMC2168496
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01030-07
Performance of a pneumolysin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of pneumococcal infections
Abstract
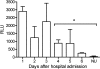
A pneumolysin-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (PLY-ELISA) for the detection of pneumolysin in urine was developed and evaluated in comparison with the commercially available Binax Now Streptococcus pneumoniae test (Binax, Portland, ME) for the diagnosis of pneumococcal infections. Assay sensitivity was evaluated using urine from 108 patients with culture-confirmed pneumococcal infections. In adults, the sensitivity and specificity of the PLY-ELISA were 56.6% and 92.2%, respectively. In children with nasopharyngeal pneumococcal carriage, PLY-ELISA and Binax Now S. pneumoniae test sensitivities were 62.5% and 87.5%, respectively, while specificities were 94.4% and 27.8%, respectively. In children with nonnasopharyngeal pneumococcal carriage, PLY-ELISA and Binax Now S. pneumoniae test sensitivities were 68.7% and 93.7%, respectively, and test specificities were 94.1% and 41.2%, respectively. The persistence of pneumolysin in urine of pneumococcal pneumonia patients decreased significantly after 4 to 6 days of treatment. Our data suggest that combining the high specificity of the PLY-ELISA with the high sensitivity of the Binax Now S. pneumoniae test would enable pneumococcal infections to be accurately diagnosed in children.
Figures
References
-
- Adegbola, R. A., S. K. Obaro, E. Biney, and B. M. Greenwood. 2001. Evaluation of Binax NOW Streptococcus pneumoniae urinary antigen test in children in a community with a high carriage rate of pneumococcus. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 20:718-719. - PubMed
-
- Andreo, F., J. Domínguez, J. Ruiz, S. Blanco, E. Arellano, C. Prat, J. Morera, and V. Ausina. 2006. Impact of rapid urine antigen tests to determine the etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Respir. Med. 100:884-891. - PubMed
-
- Charkaluk, M. L., N. Kalach, H. Mvogo, E. Dehecq, H. Magentie, J. Raymond, D. Gendrel, O. Kremp, and A. Decoster. 2006. Assessment of a rapid urinary antigen detection by an immunochromatographic test for diagnosis of pneumococcal infection in children. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 55:89-94. - PubMed
-
- Cima-Cabal, M. D., F. J. Méndez, F. Vázquez, M. M. García-Suárez, and J. R. de los Toyos. 2001. A specific and ultrasensitive chemiluminescent sandwich ELISA test for the detection and quantitation of pneumolysin. J. Immunoassay Immunochem. 22:99-112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

