Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor on intercostal nerve presenting as paraneoplastic pemphigus with fatal pulmonary involvement
- PMID: 17728520
- PMCID: PMC2693830
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.4.735
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor on intercostal nerve presenting as paraneoplastic pemphigus with fatal pulmonary involvement
Abstract
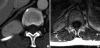
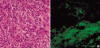
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors (IMTs) are benign neoplasms that can occur at different anatomic sites with nonspecific clinical symptoms. A 48-yr-old woman presented with a 2-month history of a relapsed oral ulcer, progressive dyspnea, and a thoracic pain induced by breathing. A tumorous mass was noticed in the right costodiaphragmatic recess on chest computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, and the patient underwent a right costotransversectomy with excision of the tumor, which originated from the 12th intercostal nerve. Histology and immunohistochemistry showed that the tumor was an IMT of the intercostal nerve. The patient's postoperative course was not favorable; dyspnea persisted after surgery, and a progressive pulmonary compromise developed. The cause of the respiratory failure was found to be bronchiolitis obliterans, which in this case proved to be a fatal complication of paraneoplastic pemphigus associated with an IMT. This case of IMT of the spinal nerve in the paravertebral region is unique in terms of its location and presentation in combination with paraneoplastic pemphigus, which is rare. A brief review of the heterogeneous theories concerning the pathogenesis, clinicopathological features, and differential diagnosis of this disease entity is presented.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inflammatory pseudotumor of the spinal nerve complicated by paraneoplastic pemphigus. Case illustration.J Neurosurg Spine. 2006 Jun;4(6):514. doi: 10.3171/spi.2006.4.6.514. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006. PMID: 16776366 No abstract available.
-
Paraneoplastic pemphigus associated with inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor.Int J Dermatol. 2006 Nov;45(11):1394-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.03109.x. Int J Dermatol. 2006. PMID: 17076745 No abstract available.
-
[Paraneoplastic pemphigus revealing dendritic cell sarcoma originating from Castleman's disease of the neck].Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2005 Jan;132(1):41-4. doi: 10.1016/s0151-9638(05)79195-x. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2005. PMID: 15746607 French.
-
Paraneoplastic pemphigus associated with inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour of the mediastinum: A favourable response to treatment and review of the literature.Australas J Dermatol. 2015 May;56(2):120-3. doi: 10.1111/ajd.12264. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Australas J Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25369175 Review.
-
Paraneoplastic pemphigus (paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome): clinical presentations and pathogenesis.Dermatol Clin. 2011 Jul;29(3):419-25, viii. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2011.03.018. Dermatol Clin. 2011. PMID: 21605807 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural system antigens are recognized by autoantibodies from patients affected by a new variant of endemic pemphigus foliaceus in Colombia.J Clin Immunol. 2011 Jun;31(3):356-68. doi: 10.1007/s10875-010-9495-1. Epub 2011 Jan 6. J Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21210298 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor presenting as paraneoplastic pemphigus in a 7-year-old girl.JAAD Case Rep. 2016 Jan 26;2(1):37-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.10.009. eCollection 2016 Jan. JAAD Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27051823 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Paraneoplastic Pemphigus with Underlying Retroperitoneal Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2017 Nov-Dec;8(6):478-481. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_17_17. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2017. PMID: 29204394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Narla LD, Newman B, Spottswood SS, Narla S, Kolli R. Inflammatory pseudotumor. Radiographics. 2003;23:719–729. - PubMed
-
- Anthony PP. Inflammatory pseudotumour (plasma cell granuloma) of lung, liver and other organs. Histopathology. 1993;23:501–503. - PubMed
-
- Dehner LP. The enigmatic inflammatory pseudotumors: the current state of our understanding, or misunderstanding (editorial) J Pathol. 2000;192:277–279. - PubMed
-
- Despeyroux-Ewers M, Catalaa I, Collin L, Cognard C, Loubes-Lacroix F, Manelfe C. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour of the spinal cord: case report and review of the literature. Neuroradiology. 2003;45:812–817. - PubMed
-
- Kim YO, Cho YJ, Ahn SK, Hwang JH, Ahn MS, Choi YH. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the thoracic spinal cord meninges: A case report. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 1998;27:1419–1423.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

