Non-HFE haemochromatosis
- PMID: 17729390
- PMCID: PMC4611190
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i35.4690
Non-HFE haemochromatosis
Abstract
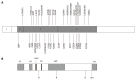
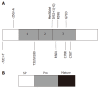
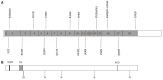
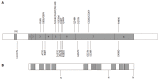
Non-HFE hereditary haemochromatosis (HH) refers to a genetically heterogeneous group of iron overload disorders that are unlinked to mutations in the HFE gene. The four main types of non-HFE HH are caused by mutations in the hemojuvelin, hepcidin, transferrin receptor 2 and ferroportin genes. Juvenile haemochromatosis is an autosomal recessive disorder and can be caused by mutations in either hemojuvelin or hepcidin. An adult onset form of HH similar to HFE-HH is caused by homozygosity for mutations in transferrin receptor 2. The autosomal dominant iron overload disorder ferroportin disease is caused by mutations in the iron exporter ferroportin. The clinical characteristics and molecular basis of the various types of non-HFE haemochromatosis are reviewed. The study of these disorders and the molecules involved has been invaluable in improving our understanding of the mechanisms involved in the regulation of iron metabolism.
Figures
References
-
- Feder JN, Gnirke A, Thomas W, Tsuchihashi Z, Ruddy DA, Basava A, Dormishian F, Domingo R, Ellis MC, Fullan A, et al. A novel MHC class I-like gene is mutated in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis. Nat Genet. 1996;13:399–408. - PubMed
-
- Piperno A, Sampietro M, Pietrangelo A, Arosio C, Lupica L, Montosi G, Vergani A, Fraquelli M, Girelli D, Pasquero P, et al. Heterogeneity of hemochromatosis in Italy. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:996–1002. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi H, Wakusawa S, Motonishi S, Miyamoto K, Okada H, Inagaki Y, Ikeda T. Genetic background of primary iron overload syndromes in Japan. Intern Med. 2006;45:1107–1111. - PubMed
-
- Roetto A, Papanikolaou G, Politou M, Alberti F, Girelli D, Christakis J, Loukopoulos D, Camaschella C. Mutant antimicrobial peptide hepcidin is associated with severe juvenile hemochromatosis. Nat Genet. 2003;33:21–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

