Iron overload and cofactors with special reference to alcohol, hepatitis C virus infection and steatosis/insulin resistance
- PMID: 17729391
- PMCID: PMC4611191
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i35.4699
Iron overload and cofactors with special reference to alcohol, hepatitis C virus infection and steatosis/insulin resistance
Abstract
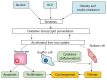
There are several cofactors which affect body iron metabolism and accelerate iron overload. Alcohol and hepatic viral infections are the most typical examples for clarifying the role of cofactors in iron overload. In these conditions, iron is deposited in hepatocytes and Kupffer cells and reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced through Fenton reaction have key role to facilitate cellular uptake of transferrin-bound iron. Furthermore, hepcidin, antimicrobial peptide produced mainly in the liver is also responsible for intestinal iron absorption and reticuloendothelial iron release. In patients with ceruloplasmin deficiency, anemia and secondary iron overload in liver and neurodegeneration are reported. Furthermore, there is accumulating evidence that fatty acid accumulation without alcohol and obesity itself modifies iron overload states. Ineffective erythropoiesis is also an important factor to accelerate iron overload, which is associated with diseases such as thalassemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. When this condition persists, the dietary iron absorption is increased due to the increment of bone marrow erythropoiesis and tissue iron overload will thereafter occurs. In porphyria cutanea tarda, iron is secondarily accumulated in the liver.
Figures
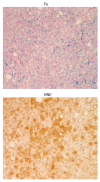
Similar articles
-
[The effect of alcohol on the regulation of iron metabolism].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008 Sep;25(147):273-5. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008. PMID: 19112848 Review. Polish.
-
High-fat, high-fructose diet induces hepatic iron overload via a hepcidin-independent mechanism prior to the onset of liver steatosis and insulin resistance in mice.Metabolism. 2013 Jan;62(1):62-9. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2012.06.008. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 22854109
-
Revaluation of clinical and histological criteria for diagnosis of dysmetabolic iron overload syndrome.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Aug 14;14(30):4745-52. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.4745. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18720534 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperferritinemia, iron overload, and multiple metabolic alterations identify patients at risk for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 Aug;96(8):2448-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.04052.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11513189
-
Clinical relevance of anemia and transfusion iron overload in myelodysplastic syndromes.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2008:166-75. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2008.1.166. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2008. PMID: 19074076 Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol Exposure Induces Depressive and Anxiety-like Behaviors via Activating Ferroptosis in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13828. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213828. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430312 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the factors associated with circulating soluble CD36 levels in patients with HCV-related chronic liver disease.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2013 Sep 9;5(1):51. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-5-51. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2013. PMID: 24016701 Free PMC article.
-
Iron overload is not the same everywhere: Particularities of iron-metabolism gene mutations in Brazil and a proposal for the investigation and management of iron overload in this population.Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2025 Apr-Jun;47(2):103846. doi: 10.1016/j.htct.2025.103846. Epub 2025 May 15. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2025. PMID: 40378601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Measurement of serum hepcidin-25 levels as a potential test for diagnosing hemochromatosis and related disorders.J Gastroenterol. 2010 Nov;45(11):1163-71. doi: 10.1007/s00535-010-0259-8. Epub 2010 Jun 9. J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20533066
-
Polydatin Prevents Electron Transport Chain Dysfunction and ROS Overproduction Paralleled by an Improvement in Lipid Peroxidation and Cardiolipin Levels in Iron-Overloaded Rat Liver Mitochondria.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 16;25(20):11104. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011104. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alla V, Bonkovsky HL. Iron in nonhemochromatotic liver disorders. Semin Liver Dis. 2005;25:461–472. - PubMed
-
- Chitturi S, George J. Interaction of iron, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2003;5:18–25. - PubMed
-
- Ortiz V, Berenguer M, Rayón JM, Carrasco D, Berenguer J. Contribution of obesity to hepatitis C-related fibrosis progression. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:2408–2414. - PubMed
-
- Barton JC, Edwards CQ. Hemochromatosis. Cambridge University Press. 2000:435–467.
-
- Cohen AR. New advances in iron chelation therapy. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2006:42–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

