Apparent heterogeneity of cardiac A1 adenosine receptors as revealed by radioligand binding experiments on N-ethylmaleimide-treated membranes
- PMID: 1775196
- PMCID: PMC5870127
- DOI: 10.1007/BF00174747
Apparent heterogeneity of cardiac A1 adenosine receptors as revealed by radioligand binding experiments on N-ethylmaleimide-treated membranes
Abstract
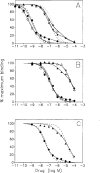
While G protein-coupled receptors are often studied by analyzing antagonist radioligand: "cold" agonist inhibition curves using an independent site model, it is now clear that KL and KH values determined in these analyses are not reliable estimates of the affinities of the agonists for "free" and G protein-coupled forms of the receptor. Thus, such experiments cannot be used to contrast the characteristics of a given type of receptor in different tissues, i.e., to probe for the existence of receptor subtypes. Since treatment with N-ethylmaleimide treatment blocks receptor: Gi/Go protein interactions, such analyses on N-ethylmaleimide-pretreated membranes should allow direct assessment of the affinities of competing ligands for the free receptor or for multiple receptor subtypes. As A1 adenosine receptors couple to Gi, and perhaps to Go, we have performed A1 adenosine receptor radioligand "competition" studies first on control, then on N-ethylmaleimide-pretreated bovine cardiac and cerebral cortical membranes. Results of experiments with the antagonist radioligand [3H]xanthine amine congener appeared to be confounded by ligand binding to A2 adenosine receptors present in the cardiac membrane preparations. Further experiments utilized the A1-specific radioligand [3H]1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine. These experiments confirmed once more that the KL values determined by computer analysis of "competition" curves performed on control membranes are not reliable estimates of the affinities of the competing ligand for free receptors.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Figures
References
-
- Abramson SN, McGonigle P, Molinoff PB. Evaluation of models for analysis of radioligand binding data. Mol Pharmacol. 1987;31:103–111. - PubMed
-
- Asano T, Ogasawara N. Uncoupling of γ-aminobutyric acid B receptors from GTP-binding proteins by N-ethylmaleimide: Effect of ethylmaleimide on purified GTP-binding proteins. Mol Pharmacol. 1986;29:244–249. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Bruns RF, Fergus JH, Badger EW, Bristol JA, Santay LA, Hartman JD, Hays SJ, Huang CC. Binding of the A1-selective adenosine antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-l,3-dipropylxanthine to rat brain membranes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Pharmacol. 1987;335:59–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
