Physiological polyamines: simple primordial stress molecules
- PMID: 17760833
- PMCID: PMC3823250
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00077.x
Physiological polyamines: simple primordial stress molecules
Abstract
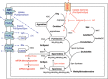
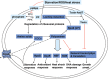
Physiological polyamines are ubiquitous polycations with pleiotropic biochemical activities, including regulation of gene expression, cell proliferation and modulation of cell signalling. Reports that the polyamines with cytoprotective activities were induced by diverse stresses raised the hypothesis that physiological polyamines may play a role in inducing stress response. In a wide range of organisms, physiological polyamines were not only induced by diverse stresses, such as reactive oxygen species (ROS), heat, ultraviolet (UV) and psychiatric stress but were able to confer beneficial effects for survival. Recent biochemical and genetic evidences show that polyamines can function as an ROS scavenger, acid tolerance factor and chemical chaperone, and positive regulators for expression of stress response genes which may explain their protective functions against diverse stresses. Taken together, these data suggest that physiological polyamines can function as primordial stress molecules in bacteria, plants and mammals, and may play an essential role in regulation of pathogen-host interactions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polyamines: molecules with regulatory functions in plant abiotic stress tolerance.Planta. 2010 May;231(6):1237-49. doi: 10.1007/s00425-010-1130-0. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Planta. 2010. PMID: 20221631 Review.
-
Polyamines and abiotic stress: recent advances.Amino Acids. 2008 Jan;34(1):35-45. doi: 10.1007/s00726-007-0501-8. Epub 2007 Mar 14. Amino Acids. 2008. PMID: 17356805 Review.
-
Improvement of plant abiotic stress tolerance through modulation of the polyamine pathway.J Integr Plant Biol. 2014 Feb;56(2):114-21. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12128. Epub 2014 Jan 8. J Integr Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 24401132 Review.
-
Emerging Role of Polyamines in Plant Stress Tolerance.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018;19(11):1114-1123. doi: 10.2174/1389203719666180718124211. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018. PMID: 30019643 Review.
-
Polyamines: essential factors for growth and survival.Planta. 2008 Aug;228(3):367-81. doi: 10.1007/s00425-008-0772-7. Epub 2008 Jul 2. Planta. 2008. PMID: 18594857 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular polyamines condense hyperphosphorylated Tau, triggering Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 22;10(1):10098. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67119-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32572101 Free PMC article.
-
Heat-responsive and time-resolved transcriptome and metabolome analyses of Escherichia coli uncover thermo-tolerant mechanisms.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 19;10(1):17715. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74606-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33077799 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine and the metabolic regulation of nitric oxide synthesis in cancer.Dis Model Mech. 2018 Aug 6;11(8):dmm033332. doi: 10.1242/dmm.033332. Dis Model Mech. 2018. PMID: 30082427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Impaired Polyamine Transport on Pneumococcal Transcriptome.Pathogens. 2021 Oct 14;10(10):1322. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10101322. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34684271 Free PMC article.
-
The use of human induced pluripotent stem cells to screen for developmental toxicity potential indicates reduced potential for non-combusted products, when compared to cigarettes.Curr Res Toxicol. 2020 Nov 15;1:161-173. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2020.11.001. eCollection 2020 Jun 10. Curr Res Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 34345845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Umekage S, Ueda T. Spermidine inhibits transient and stable ribosome subunit dissociation. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:1222–6. - PubMed
-
- Stephenson AH, Christian JF, Seidel ER. Polyamines regulate eukaryotic initiation factor 4Ebinding protein 1 gene transcription. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;323:204–12. - PubMed
-
- Kim SW, Mangold U, Waghorne C, Mobascher A, Shantz L, Banyard J, Zetter BR. Regulation of cell proliferation by the antizyme inhibitor: evidence for an antizyme-independent mechanism. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:2583–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

