Two human ARFGAPs associated with COP-I-coated vesicles
- PMID: 17760859
- PMCID: PMC2171037
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00631.x
Two human ARFGAPs associated with COP-I-coated vesicles
Abstract
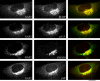
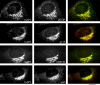
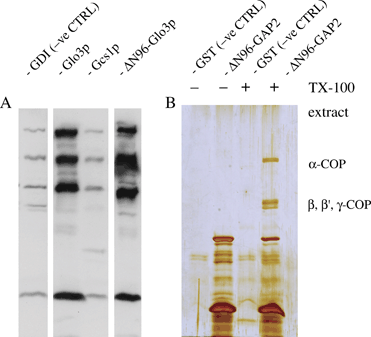
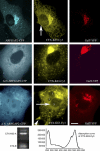
ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs) are critical regulators of vesicular trafficking pathways and act at multiple intracellular sites. ADP-ribosylation factor-GTPase-activating proteins (ARFGAPs) are proposed to contribute to site-specific regulation. In yeast, two distinct proteins, Glo3p and Gcs1p, together provide overlapping, essential ARFGAP function required for coat protein (COP)-I-dependent trafficking. In mammalian cells, only the Gcs1p orthologue, named ARFGAP1, has been characterized in detail. However, Glo3p is known to make the stronger contribution to COP I traffic in yeast. Here, based on a conserved signature motif close to the carboxy terminus, we identify ARFGAP2 and ARFGAP3 as the human orthologues of yeast Glo3p. By immunofluorescence (IF), ARFGAP2 and ARFGAP3 are closely colocalized with coatomer subunits in NRK cells in the Golgi complex and peripheral punctate structures. In contrast to ARFGAP1, both ARFGAP2 and ARFGAP3 are associated with COP-I-coated vesicles generated from Golgi membranes in the presence of GTP-gamma-S in vitro. ARFGAP2 lacking its zinc finger domain directly binds to coatomer. Expression of this truncated mutant (DeltaN-ARFGAP2) inhibits COP-I-dependent Golgi-to-endoplasmic reticulum transport of cholera toxin (CTX-K63) in vivo. Silencing of ARFGAP1 or a combination of ARFGAP2 and ARFGAP3 in HeLa cells does not decrease cell viability. However, silencing all three ARFGAPs causes cell death. Our data provide strong evidence that ARFGAP2 and ARFGAP3 function in COP I traffic.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Three homologous ArfGAPs participate in coat protein I-mediated transport.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 15;284(20):13948-13957. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900749200. Epub 2009 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19299515 Free PMC article.
-
ARFGAP2 and ARFGAP3 are essential for COPI coat assembly on the Golgi membrane of living cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 19;285(47):36709-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.180380. Epub 2010 Sep 21. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20858901 Free PMC article.
-
Differential roles of ArfGAP1, ArfGAP2, and ArfGAP3 in COPI trafficking.J Cell Biol. 2008 Nov 17;183(4):725-35. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200806140. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 19015319 Free PMC article.
-
[Retrograde transport].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2004 May;49(7 Suppl):914-5. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2004. PMID: 15168491 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
ArfGAP1 function in COPI mediated membrane traffic: currently debated models and comparison to other coat-binding ArfGAPs.Histol Histopathol. 2012 Sep;27(9):1143-53. doi: 10.14670/HH-27.1143. Histol Histopathol. 2012. PMID: 22806901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ArfGAP1 promotes COPI vesicle formation by facilitating coatomer polymerization.Cell Logist. 2011 Jul-Dec;1(4):139-154. doi: 10.4161/cl.1.4.18896. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Cell Logist. 2011. PMID: 22279613 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic analysis of Arf GAP1 indicates a regulatory role for coatomer.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 8;283(32):21965-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802268200. Epub 2008 Jun 9. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18541532 Free PMC article.
-
Three homologous ArfGAPs participate in coat protein I-mediated transport.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 15;284(20):13948-13957. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900749200. Epub 2009 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19299515 Free PMC article.
-
ARFGAP1 is dynamically associated with lipid droplets in hepatocytes.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 14;9(11):e111309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111309. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25397679 Free PMC article.
-
Targets and Potential Mechanism of Chondroitin Sulfate A-selenium Nanoparticle on Kashin-Beck Disease Chondrocytes.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Mar 26. doi: 10.1007/s12011-025-04584-3. Online ahead of print. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 40138104
References
-
- Kirchhausen T. Three ways to make a vesicle. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:187–198. - PubMed
-
- Bonifacino JS, Lippincott-Schwartz J. Coat proteins: shaping membrane transport. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:409–414. - PubMed
-
- Duden R. ER-to-Golgi transport: COP I & COP II function. Mol Membr Biol. 2003;20:197–207. - PubMed
-
- Rothman JE, Wieland FT. Protein sorting by transport vesicles. Science. 1996;272:227–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

