4G/5G plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 polymorphisms and haplotypes are associated with pneumonia
- PMID: 17761618
- PMCID: PMC2176102
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200605-644OC
4G/5G plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 polymorphisms and haplotypes are associated with pneumonia
Abstract
Rationale: Plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI)-1 inhibits urokinase and tissue plasminogen activator, required for host response to infection. Whether variation within the PAI-1 gene is associated with increased susceptibility to infection is unknown.
Objectives: To ascertain the role of the 4G/5G polymorphism and other genetic variants within the PAI-1 gene. We hypothesized that variants associated with increased PAI-1 expression would be associated with an increased occurrence of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP).
Methods: Longitudinal analysis (>12 yr) of the Health, Aging, and Body Composition cohort, aged 65-74 years at start of analysis.
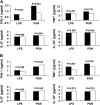
Measurements and main results: We genotyped the 4G/5G PAI-1 polymorphism and six additional single nucleotide polymorphisms. Of the 3,075 subjects, 272 (8.8%) had at least one hospitalization for CAP. Among whites, variants at the PAI4G,5G, PAI2846, and PAI7343 sites had higher risk of CAP (P = 0.018, 0.021, and 0.021, respectively). At these sites, variants associated with higher PAI-1 expression were associated with increased CAP susceptibility. Compared with the 5G/5G genotypes at PAI4G,5G site, the 4G/4G and 4G/5G genotypes were associated with a 1.98-fold increased risk of CAP (95% confidence interval, 1.2-3.2; P = 0.006). In whole blood stimulation assay, subjects with a 4G allele had 3.3- and 1.9-fold increased PAI-1 expression (P = 0.043 and 0.034, respectively). In haplotype analysis, the 4G/G/C/A haplotype at the PAI4G,5G, PAI2846, PAI4588, and PAI7343 single nucleotide polymorphisms was associated with higher CAP susceptibility, whereas the 5G/G/C/A haplotype was associated with lower CAP susceptibility. No associations were seen among blacks.
Conclusions: Genotypes associated with increased expression of PAI-1 were associated with increased susceptibility to CAP in elderly whites.
Figures
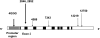

Similar articles
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 gene polymorphisms and haplotypes are associated with plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 levels but not with myocardial infarction or stroke.Am Heart J. 2006 Dec;152(6):1109-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2006.06.021. Am Heart J. 2006. PMID: 17161063
-
Promoter (4G/5G) plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 genotype and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 levels in blacks, Hispanics, and non-Hispanic whites: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study.Circulation. 2003 May 20;107(19):2422-7. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000066908.82782.3A. Epub 2003 Apr 28. Circulation. 2003. PMID: 12719278
-
Association of PAI-1 4G/5G and -844G/A gene polymorphisms and changes in PAI-1/tissue plasminogen activator levels in myocardial infarction: a case-control study.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2010 Feb;14(1):23-7. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2009.0039. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2010. PMID: 19929406
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) 4G/5G promoter polymorphisms and risk of venous thromboembolism - a meta-analysis and systematic review.Vasa. 2020 Mar;49(2):141-146. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000839. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Vasa. 2020. PMID: 31920171
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 4G/5G and the MTHFR 677C/T polymorphisms and susceptibility to polycystic ovary syndrome: a meta-analysis.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014 Apr;175:8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.12.030. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014. PMID: 24439532 Review.
Cited by
-
Ecogenomics of respiratory diseases of public health significance.Annu Rev Public Health. 2010;31:37-51 1 p following 51. doi: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.012809.103633. Annu Rev Public Health. 2010. PMID: 20070197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of biomarkers in community-acquired pneumonia: predicting mortality and response to adjunctive therapy.Crit Care. 2008;12 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):S5. doi: 10.1186/cc7028. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Crit Care. 2008. PMID: 19105798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical review: the role of biomarkers in the diagnosis and management of community-acquired pneumonia.Crit Care. 2010;14(1):203. doi: 10.1186/cc8155. Epub 2010 Feb 8. Crit Care. 2010. PMID: 20236471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of statistical methods for estimating genetic admixture in a lung cancer study of African Americans and Latinos.Am J Epidemiol. 2008 Nov 1;168(9):1035-46. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwn224. Epub 2008 Sep 12. Am J Epidemiol. 2008. PMID: 18791191 Free PMC article.
-
4G/5G polymorphism of PAI-1 gene is associated with multiple organ dysfunction and septic shock in pneumonia induced severe sepsis: prospective, observational, genetic study.Crit Care. 2010;14(2):R79. doi: 10.1186/cc8992. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Crit Care. 2010. PMID: 20429897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horrevoets AJ. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1): in vitro activities and clinical relevance. Br J Haematol 2004;125:12–23. - PubMed
-
- Abraham E. Coagulation abnormalities in acute lung injury and sepsis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2000;22:401–404. - PubMed
-
- Choi G, Schultz MJ, van Till JW, Bresser P, Van Der Zee JS, Boermeester MA, Levi M, van der Poll T. Disturbed alveolar fibrin turnover during pneumonia is restricted to the site of infection. Eur Respir J 2004;24:786–789. - PubMed
-
- Prabhakaran P, Ware LB, White KE, Cross MT, Matthay MA, Olman MA. Elevated levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in pulmonary edema fluid are associated with mortality in acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2003;285:L20–L28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

