Neuron type-specific effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat superficial dorsal horn and their relevance to 'central sensitization'
- PMID: 17761774
- PMCID: PMC2277149
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.141267
Neuron type-specific effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat superficial dorsal horn and their relevance to 'central sensitization'
Abstract
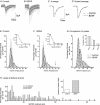
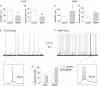
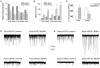
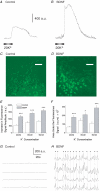
Chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the rat sciatic nerve increases the excitability of the spinal dorsal horn. This 'central sensitization' leads to pain behaviours analogous to human neuropathic pain. We have established that CCI increases excitatory synaptic drive to putative excitatory, 'delay' firing neurons in the substantia gelatinosa but attenuates that to putative inhibitory, 'tonic' firing neurons. Here, we use a defined-medium organotypic culture (DMOTC) system to investigate the long-term actions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) as a possible instigator of these changes. The age of the cultures and their 5-6 day exposure to BDNF paralleled the protocol used for CCI in vivo. Effects of BDNF (200 ng ml(-1)) in DMOTC were reminiscent of those seen with CCI in vivo. These included decreased synaptic drive to 'tonic' neurons and increased synaptic drive to 'delay' neurons with only small effects on their membrane excitability. Actions of BDNF on 'delay' neurons were exclusively presynaptic and involved increased mEPSC frequency and amplitude without changes in the function of postsynaptic AMPA receptors. By contrast, BDNF exerted both pre- and postsynaptic actions on 'tonic' cells; mEPSC frequency and amplitude were decreased and the decay time constant reduced by 35%. These selective and differential actions of BDNF on excitatory and inhibitory neurons contributed to a global increase in dorsal horn network excitability as assessed by the amplitude of depolarization-induced increases in intracellular Ca(2+). Such changes and their underlying cellular mechanisms are likely to contribute to CCI-induced 'central sensitization' and hence to the onset of neuropathic pain.
Figures



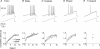
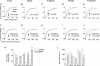

Similar articles
-
Long-term effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on the frequency of inhibitory synaptic events in the rat superficial dorsal horn.Neuroscience. 2009 Jul 21;161(4):1135-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.04.030. Epub 2009 Apr 17. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19376198
-
Contribution of the spinal cord BDNF to the development of neuropathic pain by activation of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in rats with spinal nerve ligation.Exp Neurol. 2010 Apr;222(2):256-66. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.01.003. Epub 2010 Jan 14. Exp Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20079352
-
Long-term actions of BDNF on inhibitory synaptic transmission in identified neurons of the rat substantia gelatinosa.J Neurophysiol. 2012 Jul;108(2):441-52. doi: 10.1152/jn.00457.2011. Epub 2012 Apr 11. J Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22496528
-
Is BDNF sufficient for information transfer between microglia and dorsal horn neurons during the onset of central sensitization?Mol Pain. 2010 Jul 23;6:44. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-44. Mol Pain. 2010. PMID: 20653959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF: no gain without pain?Neuroscience. 2014 Dec 26;283:107-23. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.044. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24887639 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial superoxide increases excitatory synaptic strength in spinal dorsal horn neurons of neuropathic mice.Mol Pain. 2018 Jan-Dec;14:1744806918797032. doi: 10.1177/1744806918797032. Mol Pain. 2018. PMID: 30152257 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathic pain; what we know and what we should do about it.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 22;4:1220034. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2023.1220034. eCollection 2023. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37810432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
K+ Channels in Primary Afferents and Their Role in Nerve Injury-Induced Pain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Sep 17;14:566418. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.566418. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33093824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF as a biomarker for neuropathic pain: Consideration of mechanisms of action and associated measurement challenges.Brain Behav. 2023 Mar;13(3):e2903. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2903. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 36722793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP receptors gate microglia signaling in neuropathic pain.Exp Neurol. 2012 Apr;234(2):354-61. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.11.012. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22116040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarez FJ, Villalba RM, Zerda R, Schneider SP. Vesicular glutamate transporters in the spinal cord, with special reference to sensory primary afferent synapses. J Comp Neurol. 2004;472:257–280. - PubMed
-
- Apfel SC, Wright DE, Wiideman AM, Dormia C, Snider WD, Kessler JA. Nerve growth factor regulates the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in the peripheral nervous system. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996;7:134–142. - PubMed
-
- Baba H, Ji RR, Kohno T, Moore KA, Ataka T, Wakai A, Okamoto M, Woolf CJ. Removal of GABAergic inhibition facilitates polysynaptic A fiber-mediated excitatory transmission to the superficial spinal dorsal horn. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003;24:818–830. - PubMed
-
- Bailey AL, Ribeiro-da-Silva A. Transient loss of terminals from non-peptidergic nociceptive fibers in the substantia gelatinosa of spinal cord following chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. Neuroscience. 2006;138:675–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

