The Akt pathway regulates survival and homing in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
- PMID: 17761832
- PMCID: PMC2234792
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-092098
The Akt pathway regulates survival and homing in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
Abstract
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (WM) is an incurable low-grade lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. We demonstrate up-regulated Akt activity in WM, and that Akt down-regulation by Akt knockdown and the inhibitor perifosine leads to significant inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in WM cells in vitro, but not in normal donor peripheral blood and hematopoietic progenitors. Importantly, down-regulation of Akt induced cytotoxicity of WM cells in the bone marrow microenvironment (BMM) context. Perifosine induced significant reduction in WM tumor growth in vivo in a subcutaneous xenograft model through inhibition of Akt phosphorylation and downstream targets. We also demonstrated that Akt pathway down-regulation inhibited migration and adhesion in vitro and homing of WM tumor cells to the BMM in vivo. Proteomic analysis identified other signaling pathways modulated by perifosine, such as activation of ERK MAPK pathway, which induces survival of tumor cells. Interestingly, MEK inhibitor significantly enhanced perifosine-induced cytotoxicity in WM cells. Using Akt knockdown experiments and specific Akt and PI3K inhibitors, we demonstrated that ERK activation is through a direct effect, rather than feedback activation, of perifosine upstream ERK pathway. These results provide understanding of biological effects of Akt pathway in WM and provide the framework for clinical evaluation of perifosine in WM patients.
Figures
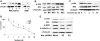

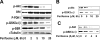

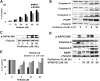
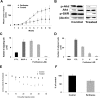
 ) or untreated control (
) or untreated control ( ), were injected in the tail vein of 2 balb/c mice. Cells were counted every 5 minutes for 1 hour. The cell count decreased by 75% in the control and only by 40% in the treated mouse, P = .001. (F) Histogram showing that the number of cells present in the perivascular bone marrow niches of the skull was significantly higher in the control mice compared with the perifosine-treated group at 24 hours after injection (P = .039), using in vivo confocal imaging of quadrants 3 and 4 of the skull of mice.
), were injected in the tail vein of 2 balb/c mice. Cells were counted every 5 minutes for 1 hour. The cell count decreased by 75% in the control and only by 40% in the treated mouse, P = .001. (F) Histogram showing that the number of cells present in the perivascular bone marrow niches of the skull was significantly higher in the control mice compared with the perifosine-treated group at 24 hours after injection (P = .039), using in vivo confocal imaging of quadrants 3 and 4 of the skull of mice.
References
-
- Ghobrial IM, Gertz MA, Fonseca R. Waldenstrom macroglobulinaemia. Lancet Oncol. 2003;4:679–685. - PubMed
-
- Owen RG, Treon SP, Al-Katib A, et al. Clinicopathological definition of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia: consensus panel recommendations from the Second International Workshop on Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia. Semin Oncol. 2003;30:110–115. - PubMed
-
- Treon SP, Dimopoulos M, Kyle RA. Defining Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. Semin Oncol. 2003;30:107–109. - PubMed
-
- Gertz MA, Anagnostopoulos A, Anderson K, et al. Treatment recommendations in Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia: consensus panel recommendations from the Second International Workshop on Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia. Semin Oncol. 2003;30:121–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

