Pomegranate polyphenols and resveratrol protect the neonatal brain against hypoxic-ischemic injury
- PMID: 17762204
- PMCID: PMC3066259
- DOI: 10.1159/000105477
Pomegranate polyphenols and resveratrol protect the neonatal brain against hypoxic-ischemic injury
Abstract
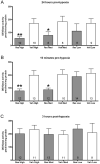
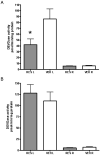
A previous study from our lab has shown that the polyphenol-rich pomegranate juice can protect the neonatal mouse brain against hypoxic-ischemic (H-I) injury when given to mothers in their drinking water. To test the hypothesis that this protection is due to the polyphenols in the juice, we studied the effects of the pomegranate polyphenol extract in the same neonatal H-I model. To further explore the role of a specific polyphenol in neonatal H-I we investigated the effects of resveratrol. The neuroprotective effects of resveratrol have been demonstrated in adult models of stroke, but had not previously been examined in neonates. We show that pomegranate polyphenols and resveratrol reduce caspase-3 activation following neonatal H-I. Resveratrol reduced caspase-3 activation when given before the injury but not when given 3 h after the injury. In addition to preventing caspase-3 activation, resveratrol also reduced calpain activation. Finally, we show that resveratrol can protect against tissue loss measured at 7 days after the injury. These and other recent findings suggest that polyphenols should be further investigated as a potential treatment to decrease brain injury due to neonatal H-I.
2007 S. Karger AG, Basel
Figures



Similar articles
-
Maternal dietary supplementation with pomegranate juice is neuroprotective in an animal model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury.Pediatr Res. 2005 Jun;57(6):858-64. doi: 10.1203/01.PDR.0000157722.07810.15. Epub 2005 Mar 17. Pediatr Res. 2005. PMID: 15774834
-
Delayed peripheral administration of a GPE analogue induces astrogliosis and angiogenesis and reduces inflammation and brain injury following hypoxia-ischemia in the neonatal rat.Dev Neurosci. 2007;29(4-5):393-402. doi: 10.1159/000105480. Dev Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17762207
-
Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol on ischemic injury mediated by modulating the release of neurotransmitter and neuromodulator in rats.Neurochem Int. 2010 Feb;56(3):495-500. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2009.12.009. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Neurochem Int. 2010. PMID: 20026214
-
Unique properties of polyphenol stilbenes in the brain: more than direct antioxidant actions; gene/protein regulatory activity.Neurosignals. 2005;14(1-2):61-70. doi: 10.1159/000085386. Neurosignals. 2005. PMID: 15956815 Review.
-
A Review of Plant Extracts and Plant-Derived Natural Compounds in the Prevention/Treatment of Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 15;22(2):833. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020833. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33467663 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment advances in neonatal neuroprotection and neurointensive care.Lancet Neurol. 2011 Apr;10(4):372-82. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70016-3. Lancet Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21435600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pretreatment with oleuropein protects the neonatal brain from hypoxia-ischemia by inhibiting apoptosis and neuroinflammation.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025 Apr;45(4):717-734. doi: 10.1177/0271678X241270237. Epub 2024 Aug 19. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025. PMID: 39157939 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Implications of Epigenetic Dysregulation in Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage.Front Neurol. 2020 Jun 9;11:483. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00483. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32582011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphenols Mediate Neuroprotection in Cerebral Ischemic Stroke-An Update.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 23;15(5):1107. doi: 10.3390/nu15051107. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36904106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pomegranate juice augments memory and FMRI activity in middle-aged and older adults with mild memory complaints.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:946298. doi: 10.1155/2013/946298. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23970941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Shishodia S. Suppression of the nuclear factor-kappaB activation pathway by spice-derived phytochemicals: reasoning for seasoning. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1030:434–441. - PubMed
-
- Anesini C, Perez C. Screening of plants used in Argentine folk medicine for antimicrobial activity. J Ethnopharmacol. 1993;39:119–128. - PubMed
-
- Araki T, Sasaki Y, Milbrandt J. Increased nuclear NAD biosynthesis and SIRT1 activation prevent axonal degeneration. Science. 2004;305:1010–1013. - PubMed
-
- Back SA. Recent advances in human perinatal white matter injury. Prog Brain Res. 2001;132:131–147. - PubMed
-
- Back SA, Rivkees SA. Emerging concepts in periventricular white matter injury. Semin Perinatol. 2004;28:405–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

