Distinct regulation of interleukin-17 in human T helper lymphocytes
- PMID: 17763419
- PMCID: PMC2323677
- DOI: 10.1002/art.22866
Distinct regulation of interleukin-17 in human T helper lymphocytes
Abstract
Objective: Interleukin-17 (IL-17)-producing T helper cells have been proposed to represent a separate lineage of CD4+ cells, designated Th17 cells, which are regulated by the transcription factor retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gammat (RORgammat). However, despite advances in understanding murine Th17 differentiation, a systematic assessment of factors that promote the differentiation of naive human T cells to Th17 cells has not been reported. The present study was undertaken to assess the effects on naive human CD4+ T cells of cytokines known to promote murine Th17 cells.
Methods: Human naive and memory CD4+ T cells isolated from peripheral blood were activated and cultured with various cytokines. Cytokine production was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and flow cytometry. Messenger RNA was measured by quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
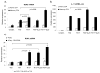
Results: In response to anti-CD3/anti-CD28 stimulation alone, human memory T cells rapidly produced IL-17, whereas naive T cells expressed low levels. Transforming growth factor beta1 and IL-6 up-regulated RORgammat expression but did not induce Th17 differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells. However, IL-23 up-regulated its own receptor and was an important inducer of IL-17 and IL-22.
Conclusion: The present data demonstrate the differential regulation of IL-17 and RORgammat expression in human CD4+ T cells compared with murine cells. Optimal conditions for the development of IL-17-producing T cells from murine naive precursors are ineffective in human T cells. Conversely, IL-23 promoted the generation of human Th17 cells but was also a very potent inducer of other proinflammatory cytokines. These findings may have important implications in the pathogenesis of human autoimmunity as compared with mouse models.
Figures
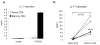




References
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986;136(7):2348–57. - PubMed
-
- Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996;383(6603):787–93. - PubMed
-
- Murphy KM, Reiner SL. The lineage decisions of helper T cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(12):933–44. - PubMed
-
- Spilianakis CG, Lalioti MD, Town T, Lee GR, Flavell RA. Interchromosomal associations between alternatively expressed loci. Nature. 2005;435(7042):637–45. - PubMed
-
- Shevach EM. Regulatory T cells in autoimmmunity*. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:423–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

