Displacement and re-accumulation of centromeric cohesin during transient pre-anaphase centromere splitting
- PMID: 17763979
- PMCID: PMC2075529
- DOI: 10.1007/s00412-007-0118-4
Displacement and re-accumulation of centromeric cohesin during transient pre-anaphase centromere splitting
Abstract
The ring-shaped cohesin complex links sister chromatids until their timely segregation during mitosis. Cohesin is enriched at centromeres where it provides the cohesive counterforce to bipolar tension produced by the mitotic spindle. As a consequence of spindle tension, centromeric sequences transiently split in pre-anaphase cells, in some organisms up to several micrometers. This 'centromere breathing' presents a paradox, how sister sequences separate where cohesin is most enriched. We now show that in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, cohesin binding diminishes over centromeric sequences that split during breathing. We see no evidence for cohesin translocation to surrounding sequences, suggesting that cohesin is removed from centromeres during breathing. Two pools of cohesin can be distinguished. Cohesin loaded before DNA replication, which has established sister chromatid cohesion, disappears during breathing. In contrast, cohesin loaded after DNA replication is partly retained. As sister centromeres re-associate after transient separation, cohesin is reloaded in a manner independent of the canonical cohesin loader Scc2/Scc4. Efficient centromere re-association requires the cohesion establishment factor Eco1, suggesting that re-establishment of sister chromatid cohesion contributes to the dynamic behaviour of centromeres in mitosis. These findings provide new insights into cohesin behaviour at centromeres.
Figures

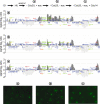



References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1126/science.1064027', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1064027'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11598266', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11598266/'}]}
- Bernard P, Maure JF, Partridge JF, Genier S, Javerzat JP, Allshire RC (2001) Requirement of heterochromatin for cohesion at centromeres. Science 294:2539–2542 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81019-3', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81019-3'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10428036', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10428036/'}]}
- Blat Y, Kleckner N (1999) Cohesins bind to preferential sites along yeast chromosome III, with differential regulation along arms versus the centric region. Cell 98:249–259 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80420-7', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80420-7'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10882066', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10882066/'}]}
- Ciosk R, Shirayama M, Shevchenko A, Tanaka T, Toth A, Shevchenko A, Nasmyth K (2000) Cohesin’s binding to chromosomes depends on a separate complex consisting of Scc2 and Scc4 proteins. Mol Cell 5:1–20 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1038/nature02328', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02328'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '14961024', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14961024/'}]}
- Dewar H, Tanaka K, Nasmyth K, Tanaka TU (2004) Tension between two kinetochores suffices for their bi-orientation on the mitotic spindle. Nature 428:93–97 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1101/gad.1498707', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1498707'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1785119', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1785119/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17242156', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17242156/'}]}
- Eckert CA, Gravdahl DJ, Megee PC (2007) The enhancement of pericentromeric cohesin association by conserved kinetochore components promotes high-fidelity chromosome segregation and is sensitive to microtubule-based tension. Genes Dev 21:278–291 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

