The effect of exercise on the absorption of inhaled human insulin in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 17764475
- PMCID: PMC2291224
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.03000.x
The effect of exercise on the absorption of inhaled human insulin in healthy volunteers
Abstract
What is already known about this subject: Exercise is known to affect absorption of other inhaled substances, but so far there are no reports on the effect of exercise on the absorption of inhaled insulin in humans.
What this paper adds: This report is the first to investigate the effect of exercise on the absorption of inhaled insulin. In this study in healthy volunteers we found that exercise early after dosing increased absorption (15-20%) of inhaled insulin over the first 2 h after start of exercise, with an approximately 30% increase in maximal insulin concentration, and unchanged overall absorption.
Aims: To investigate the effect of moderate exercise on the absorption of inhaled insulin.
Methods: A single-centre, randomized, open-label, three-period cross-over trial was carried out in 12 nonsmoking healthy subjects. A dose of 3.5 mg inhaled human insulin was administered via a nebulizer and followed in random order by either 1) no exercise (NOEX), 2) 30 min exercise starting immediately after dosing (EX0), or 3) 30 min exercise starting 30 min after dosing (EX30). The study was carried out as a 10 h euglycaemic glucose clamp (90 mg dl(-1) (5.0 mmol l(-1))).
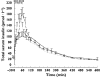
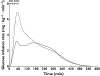
Results: The absorption of insulin over the first 2 h after start of exercise was 16% increased for EX0 (ratio (95%CI) 1.16 (1.04, 1.30), P = 0.01) and 20% increased for EX30 (1.20 (1.05, 1.36), P < 0.01), both compared with NOEX; the overall insulin absorption during 6 h and 10 h after dosing was not influenced by exercise. The maximum insulin concentration (C(max)) increased by 32% for EX0 and 35% for EX30 (both P < 0.01) compared with NOEX, while the time to C(max) was 31 min faster for EX0 (P < 0.01), but not significantly different after EX30, compared with NOEX.
Conclusions: A significant and clinically relevant increase of insulin absorption over the first 2 h after the beginning of exercise was observed. Until data from studies using the specific insulin inhalers exists, patients using inhaled insulin should be made aware of a potential increased absorption and higher concentration of insulin in connection with exercise.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of exercise on the absorption of inhaled human insulin via the AERx insulin diabetes management system in people with type 1 diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2007 Oct;30(10):2571-6. doi: 10.2337/dc06-2589. Epub 2007 Jul 9. Diabetes Care. 2007. PMID: 17620446 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of smoking cessation, acute re-exposure and nicotine replacement in smokers on AIR inhaled insulin pharmacokinetics and glucodynamics.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Apr;65(4):480-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.03041.x. Epub 2007 Oct 8. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17922880 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Acute passive cigarette smoke exposure and inhaled human insulin (Exubera) pharmacokinetics.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;65(6):864-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03122.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18477263 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Variability of insulin absorption and insulin action.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2002;4(5):673-82. doi: 10.1089/152091502320798312. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12450450 Review.
-
Insulin disposition in the lung following oral inhalation in humans : a meta-analysis of its pharmacokinetics.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2004;43(8):539-52. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200443080-00004. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2004. PMID: 15170368 Review.
References
-
- Fineberg SE. Diabetes therapy trials with inhaled insulin. Expert Opin Inv Drug. 2006;15:743–62. - PubMed
-
- Brunner GA, Balent B, Ellmerer M, Schaupp L, Siebenhofer A, Jendle JH, Okikawa J, Pieber TR. Dose–response relation of liquid aerosol inhaled insulin in type I diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2001;44:305–8. - PubMed
-
- Kapitza C, Heise T, Fishman RS, Shapiro DA, Gopalakrishnan V, Rave K, Bott S, Perera AD, Heinemann L. Impact of particle size and aerosolization time on the metabolic effect of an inhaled insulin aerosol. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2004;6:119–27. - PubMed
-
- Steiner S, Pfutzner A, Wilson BR, Harzer O, Heinemann L, Rave K. Technosphere/Insulin – proof of concept study with a new insulin formulation for pulmonary delivery. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2002;110:17–21. - PubMed
-
- Heinemann L, Traut T, Heise T. Time-action profile of inhaled insulin. Diabet Med. 1997;14:63–72. - PubMed

