High resolution melting for mutation scanning of TP53 exons 5-8
- PMID: 17764544
- PMCID: PMC2025602
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-168
High resolution melting for mutation scanning of TP53 exons 5-8
Abstract
Background: p53 is commonly inactivated by mutations in the DNA-binding domain in a wide range of cancers. As mutant p53 often influences response to therapy, effective and rapid methods to scan for mutations in TP53 are likely to be of clinical value. We therefore evaluated the use of high resolution melting (HRM) as a rapid mutation scanning tool for TP53 in tumour samples.
Methods: We designed PCR amplicons for HRM mutation scanning of TP53 exons 5 to 8 and tested them with DNA from cell lines hemizygous or homozygous for known mutations. We assessed the sensitivity of each PCR amplicon using dilutions of cell line DNA in normal wild-type DNA. We then performed a blinded assessment on ovarian tumour DNA samples that had been previously sequenced for mutations in TP53 to assess the sensitivity and positive predictive value of the HRM technique. We also performed HRM analysis on breast tumour DNA samples with unknown TP53 mutation status.
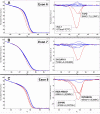
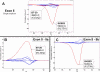
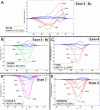
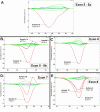
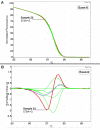
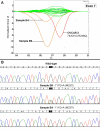
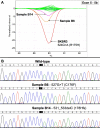
Results: One cell line mutation was not readily observed when exon 5 was amplified. As exon 5 contained multiple melting domains, we divided the exon into two amplicons for further screening. Sequence changes were also introduced into some of the primers to improve the melting characteristics of the amplicon. Aberrant HRM curves indicative of TP53 mutations were observed for each of the samples in the ovarian tumour DNA panel. Comparison of the HRM results with the sequencing results revealed that each mutation was detected by HRM in the correct exon. For the breast tumour panel, we detected seven aberrant melt profiles by HRM and subsequent sequencing confirmed the presence of these and no other mutations in the predicted exons.
Conclusion: HRM is an effective technique for simple and rapid scanning of TP53 mutations that can markedly reduce the amount of sequencing required in mutational studies of TP53.
Figures

References
-
- Deppert W, Buschhausen-Denker G, Patschinsky T, Steinmeyer K. Cell cycle control of p53 in normal (3T3) and chemically transformed (Meth A) mouse cells. II. Requirement for cell cycle progression. Oncogene. 1990;5:1701–1706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

