Rod-derived Cone Viability Factor-2 is a novel bifunctional-thioredoxin-like protein with therapeutic potential
- PMID: 17764561
- PMCID: PMC2064930
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-74
Rod-derived Cone Viability Factor-2 is a novel bifunctional-thioredoxin-like protein with therapeutic potential
Abstract
Background: Cone degeneration is the hallmark of the inherited retinal disease retinitis pigmentosa. We have previously identified a trophic factor "Rod-derived Cone Viability Factor (RdCVF) that is secreted by rods and promote cone viability in a mouse model of the disease.
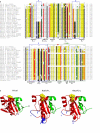
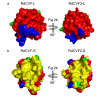
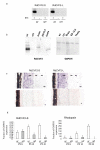
Results: Here we report the bioinformatic identification and the experimental analysis of RdCVF2, a second trophic factor belonging to the Rod-derived Cone Viability Factor family. The mouse RdCVF gene is known to be bifunctional, encoding both a long thioredoxin-like isoform (RdCVF-L) and a short isoform with trophic cone photoreceptor viability activity (RdCVF-S). RdCVF2 shares many similarities with RdCVF in terms of gene structure, expression in a rod-dependent manner and protein 3D structure. Furthermore, like RdCVF, the RdCVF2 short isoform exhibits cone rescue activity that is independent of its putative thiol-oxydoreductase activity.
Conclusion: Taken together, these findings define a new family of bifunctional genes which are: expressed in vertebrate retina, encode trophic cone viability factors, and have major therapeutic potential for human retinal neurodegenerative diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa.
Figures

References
-
- Carter-Dawson LD, LaVail MM, Sidman RL. Differential effect of the rd mutation on rods and cones in the mouse retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1978;17:489–498. - PubMed
-
- Mohand-Said S, Deudon-Combe A, Hicks D, Simonutti M, Forster V, Fintz AC, Leveillard T, Dreyfus H, Sahel JA. Normal retina releases a diffusible factor stimulating cone survival in the retinal degeneration mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:8357–8362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.14.8357. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

