Electrophysiological responses to affective stimuli in Mexican Americans: Relationship to alcohol dependence and personality traits
- PMID: 17764730
- PMCID: PMC2042967
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2007.07.019
Electrophysiological responses to affective stimuli in Mexican Americans: Relationship to alcohol dependence and personality traits
Abstract
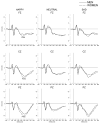
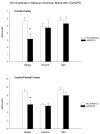
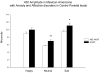
The relationship between the P450 component elicited by affective stimuli and: a personal history of alcohol dependence, antisocial personality disorder/conduct disorder (ASPD/CD) or affective anxiety disorders (ANYAXAF) was examined in Mexican Americans, a group with high rates of heavy drinking. Data from two hundred and twenty two young adults between the ages of 18 and 30 were used in the analyses. ERPs were collected using a task that required discrimination between faces with neutral, sad and happy facial expressions. DSM-IIIR diagnoses were obtained using a structured interview and personality traits were indexed using the Maudsley personality inventory. Men had significantly diminished P450 responses, when compared to women which were further reduced in men with ASPD/CD; whereas, a significant increase in P450 amplitudes was seen in those participants with ANYAXAF. P450 amplitudes were also significantly increased in men with high extraversion scores and in women with high neuroticism scores. No significant associations were seen between the P450 amplitude and the diagnosis of alcohol dependence. These data suggest that interpretations of P450 responses in Mexican Americans need to take into account the interactions between gender, the affective valence of the eliciting stimuli, as well as psychiatric status.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N4 component responses to pre-pulse startle stimuli in young adults: relationship to alcohol dependence.Psychiatry Res. 2011 Jul 30;188(2):237-44. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2011.04.010. Epub 2011 May 6. Psychiatry Res. 2011. PMID: 21550123 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological responses to affective stimuli in Southwest California Indians: relationship to alcohol dependence.J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2007 Nov;68(6):813-23. doi: 10.15288/jsad.2007.68.813. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17960299
-
CR-19-0950: Event-related responses to alcohol-related stimuli in Mexican-American young adults: Relation to age, gender, comorbidity and "dark side" symptoms.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019 Sep 1;202:76-86. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.06.001. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019. PMID: 31323376 Free PMC article.
-
Event-related oscillations to affective stimuli: heritability, linkage and relationship to externalizing disorders.J Psychiatr Res. 2012 Feb;46(2):256-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2011.10.017. Epub 2011 Nov 26. J Psychiatr Res. 2012. PMID: 22123122 Free PMC article.
-
Frontal P300 decrements, alcohol dependence, and antisocial personality disorder.Biol Psychiatry. 2000 Jun 15;47(12):1064-71. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(99)00317-0. Biol Psychiatry. 2000. PMID: 10862806 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Genetic variation in FAAH is associated with cannabis use disorders in a young adult sample of Mexican Americans.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016 Sep 1;166:249-53. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.06.021. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016. PMID: 27394933 Free PMC article.
-
CHRNA5 and CHRNA3 variants and level of neuroticism in young adult Mexican American men and women.Twin Res Hum Genet. 2014 Apr;17(2):80-8. doi: 10.1017/thg.2014.11. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24588897 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Alcohol on EEG Activity: A Systematic Review Focused on Sex-Related Differences in Youth.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025;23(6):705-727. doi: 10.2174/1570159X23666241106095027. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39506425 Free PMC article.
-
N4 component responses to pre-pulse startle stimuli in young adults: relationship to alcohol dependence.Psychiatry Res. 2011 Jul 30;188(2):237-44. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2011.04.010. Epub 2011 May 6. Psychiatry Res. 2011. PMID: 21550123 Free PMC article.
-
Event-related Oscillations to Emotional Faces are Related to a History of Internalizing Disorders.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2023 Jul;54(4):420-433. doi: 10.1177/15500594221088258. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 35379012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acton GS. Measurement of impulsivity in a hierarchical model of personality traits: implications for substance use. Subst Use Misuse. 2003;38:67–83. - PubMed
-
- Barcelo F, Suwazono S, Knight RT. Prefrontal modulation of visual processing in humans. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:399–403. - PubMed
-
- Barrett SE, Rugg MD. Event-related potentials and the semantic matching of faces. Neuropsychologia. 1989;27:913–22. - PubMed
-
- Bauer LO. Frontal P300 decrements, childhood conduct disorder, family history, and the prediction of relapse among abstinent cocaine abusers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1997;44:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Bauer LO. Differential effects of alcohol, cocaine, and opioid abuse on event-related potentials recorded during a response competition task. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2002;66:137–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

