Generation and characterization of hybridoma antibodies for immunotherapy of tularemia
- PMID: 17764754
- PMCID: PMC2128743
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imlet.2007.07.006
Generation and characterization of hybridoma antibodies for immunotherapy of tularemia
Abstract
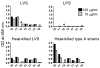
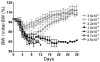
Tularemia is caused by the Gram-negative facultative intracellular bacterium Francisella tularensis, which has been classified as a category A select agent-a likely bioweapon. The high virulence of F. tularensis and the threat of engineered antibiotic resistant variants warrant the development of new therapies to combat this disease. We have characterized 14 anti-Francisella hybridoma antibodies derived from mice infected with F. tularensis live vaccine strain (LVS) for potential use as immunotherapy of tularemia. All 14 antibodies cross-reacted with virulent F. tularensis type A clinical isolates, 8 bound to a purified preparation of LVS LPS, and 6 bound to five protein antigens, identified by proteome microarray analysis. An IgG2a antibody, reactive with the LPS preparation, conferred full protection when administered either systemically or intranasally to BALB/c mice post challenge with a lethal dose of intranasal LVS; three other antibodies prolonged survival. These anti-Francisella hybridoma antibodies could be converted to chimeric versions with mouse V regions and human C regions to serve as components of a recombinant polyclonal antibody for clinical testing as immunotherapy of tularemia. The current study is the first to employ proteome microarrays to identify the target antigens of anti-Francisella monoclonal antibodies and the first to demonstrate the systemic and intranasal efficacy of monoclonal antibodies for post-exposure treatment of respiratory tularemia.
Figures

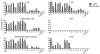
References
-
- Sjostedt A. Virulence determinants and protective antigens of Francisella tularensis. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2003;6:66–71. - PubMed
-
- Griffin KF, Oyston PC, Titball RW. Francisella tularensis vaccines. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2007;49:315–323. - PubMed
-
- Larsson P, Oyston PC, Chain P, Chu MC, Duffield M, Fuxelius HH, Garcia E, Halltorp G, Johansson D, Isherwood KE, Karp PD, Larsson E, Liu Y, Michell S, Prior J, Prior R, Malfatti S, Sjostedt A, Svensson K, Thompson N, Vergez L, Wagg JK, Wren BW, Lindler LE, Andersson SG, Forsman M, Titball RW. The complete genome sequence of Francisella tularensis, the causative agent of tularemia. Nat Genet. 2005;37:153–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

