Anxiety and orienting of gaze to angry and fearful faces
- PMID: 17764810
- PMCID: PMC2075532
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2007.07.005
Anxiety and orienting of gaze to angry and fearful faces
Abstract
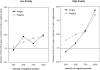
Neuroscience research indicates that individual differences in anxiety may be attributable to a neural system for threat-processing, involving the amygdala, which modulates attentional vigilance, and which is more sensitive to fearful than angry faces. Complementary cognitive studies indicate that high-anxious individuals show enhanced visuospatial orienting towards angry faces, but it is unclear whether fearful faces elicit a similar attentional bias. This study compared biases in initial orienting of gaze to fearful and angry faces, which varied in emotional intensity, in high- and low-anxious individuals. Gaze was monitored whilst participants viewed a series of face-pairs. Results showed that fearful and angry faces elicited similar attentional biases. High-anxious individuals were more likely to direct gaze at intense negative facial expressions, than low-anxious individuals, whereas the groups did not differ in orienting to mild negative expressions. Implications of the findings for research into the neural and cognitive bases of emotion processing are discussed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anxiety and sensitivity to eye gaze in emotional faces.Brain Cogn. 2006 Apr;60(3):282-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2005.05.002. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Brain Cogn. 2006. PMID: 16510226
-
Aggression differentially modulates brain responses to fearful and angry faces: an exploratory study.Neuroreport. 2015 Aug 19;26(12):663-8. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000412. Neuroreport. 2015. PMID: 26164452
-
Anxiety predicts a differential neural response to attended and unattended facial signals of anger and fear.Neuroimage. 2009 Feb 1;44(3):1144-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.09.056. Epub 2008 Oct 19. Neuroimage. 2009. PMID: 18996489
-
Eye tracking of attention in the affective disorders: a meta-analytic review and synthesis.Clin Psychol Rev. 2012 Dec;32(8):704-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2012.09.004. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Clin Psychol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23059623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonergic modulation of face-emotion recognition.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2008 Apr;41(4):263-9. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2008000400002. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2008. PMID: 18392448 Review.
Cited by
-
Emotional faces guide the eyes in the absence of awareness.Elife. 2019 Feb 8;8:e43467. doi: 10.7554/eLife.43467. Elife. 2019. PMID: 30735123 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between trait anxiety and trait anger predict amygdala reactivity to angry facial expressions in men but not women.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2012 Feb;7(2):213-21. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsq101. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 21183456 Free PMC article.
-
Vigilant attention to threat, sleep patterns, and anxiety in peripubertal youth.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018 Dec;59(12):1309-1322. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12923. Epub 2018 May 2. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29718535 Free PMC article.
-
Vigilance in the laboratory predicts avoidance in the real world: A dimensional analysis of neural, behavioral, and ecological momentary data in anxious youth.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2016 Jun;19:128-136. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27010577 Free PMC article.
-
Neurocognitive mechanisms of gaze-expression interactions in face processing and social attention.Neuropsychologia. 2012 Apr;50(5):553-66. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.01.019. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Neuropsychologia. 2012. PMID: 22285906 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams R.B., Gordon H.L., Baird A.A., Ambady N., Kleck R.E. Effects of gaze on amygdala sensitivity to anger and fear faces. Science. 2003;300:1536. - PubMed
-
- Ballenger J.C. Current treatments of anxiety disorders in adults. Biological Psychiatry. 1999;46:1579–1594. - PubMed
-
- Beck A.T., Emery G. Basic Books; New York: 1985. Anxiety Disorders and Phobias: A Cognitive Perspective.
-
- Blair R.J., Morris J.S., Frith C.D., Perrett D.I., Dolan R.J. Dissociable neural responses to facial expressions of sadness and anger. Brain. 1999;122(5):883–893. - PubMed
-
- Bradley B.P., Mogg K., Falla S.J., Hamilton L.R. Attentional bias for threatening facial expressions in anxiety: manipulation of stimulus duration. Cognition and Emotion. 1998;12:737–753.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

