Intramyocellular lipids: maker vs. marker of insulin resistance
- PMID: 17766054
- PMCID: PMC2288617
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mehy.2007.03.044
Intramyocellular lipids: maker vs. marker of insulin resistance
Abstract
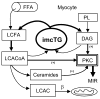
Intramyocellular triglyceride (imcTG) content in skeletal muscle is abnormally high in lipid oversupply models in obesity, type 2 diabetes (T2D) and other metabolically diseased conditions. The imcTG abnormality was also found to be significantly correlated with muscle insulin resistance (MIR). As skeletal muscle is the main site for insulin-mediated glucose utilization, the research on this topic has been active since. However, to date the pathways responsible for the imcTG excess and the mechanisms underlying the imcTG-MIR correlation have not been identified. A current view is focused on a backward mechanism that fatty acid oxidation by muscle is impaired causing imcTG to accumulate and, therefore, an enlarged imcTG pool is merely a marker of MIR. However, based on kinetic studies, it is more likely that imcTG is a source of MIR. On one hand, an enlarged and fast turning over imcTG pool interferes with insulin signaling by producing excess amounts of signaling molecules that activate PKC pathways. On the other hand, it may promote mitochondrial beta-oxidation that suppresses glucose metabolism via substrate competition. Therefore, it is hypothesized that imcTG is a source of MIR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intramyocellular lipid kinetics and insulin resistance.Lipids Health Dis. 2007 Jul 24;6:18. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-6-18. Lipids Health Dis. 2007. PMID: 17650308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscle type-dependent responses to insulin in intramyocellular triglyceride turnover in obese rats.Obes Res. 2005 Dec;13(12):2081-7. doi: 10.1038/oby.2005.258. Obes Res. 2005. PMID: 16421341
-
Fatty acids inhibit intramyocellular triglyceride synthesis and turnover acutely in high fat-fed obese rats.Horm Metab Res. 2006 Nov;38(11):721-6. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-955093. Horm Metab Res. 2006. PMID: 17111298
-
Acute hyperinsulinemia inhibits intramyocellular triglyceride synthesis in high-fat-fed obese rats.J Lipid Res. 2006 Dec;47(12):2640-6. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M600116-JLR200. Epub 2006 Sep 11. J Lipid Res. 2006. PMID: 16966492
-
Fatty acids and insulin resistance in muscle and liver.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Dec;19(4):625-35. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2005.07.003. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005. PMID: 16311221 Review.
Cited by
-
Origins of metabolic complications in obesity: adipose tissue and free fatty acid trafficking.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011 Nov;14(6):535-41. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32834ad8b6. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011. PMID: 21849896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Suppresses Adipogenesis in Pig Intramuscular Fat Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Dec 23;17(1):11. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010011. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26703591 Free PMC article.
-
1H MRS of intramyocellular lipids in soleus muscle at 7 T: spectral simplification by using long echo times without water suppression.Magn Reson Med. 2010 Sep;64(3):662-71. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22345. Magn Reson Med. 2010. PMID: 20578068 Free PMC article.
-
UCP4 overexpression improves fatty acid oxidation and insulin sensitivity in L6 myocytes.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2011 Apr;43(2):109-18. doi: 10.1007/s10863-011-9344-9. Epub 2011 May 24. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2011. PMID: 21607879
References
-
- Storlien LH, Jenkins AB, Chrisholm DJ, Pascoe WS, Khouri S, Kraegen EW. Influence of Dietary Fat Composition on Development of Insulin Resistance in Rat. Relationship to Muscle Triglyceride and Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Muscle Phospholipid. Diabetes. 1991;40:280–289. - PubMed
-
- Pan DA, Lillioja S, Kriketos AD, Milner MR, Baur LA, Bogardus C, Jenkins AB, Storlien LH. Skeletal Muscle Triglyceride Levels Are Inversely Related to Insulin Action. Diabetes. 1997;46:983–988. - PubMed
-
- Kelley DE, Goodpaster BH. Skeletal Muscle Triglyceride. An Aspect of Regional Adiposity and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:933–941. - PubMed
-
- Guo ZK, Zhou L. Evidence for Increased Insulin-Resistant Lipolysis in Skeletal Muscle of High-Fat-Fed Rats. Metabolism. 2004;53:794–798. - PubMed
-
- Perseghin G, Scifo P, De Cobelli F, Pagliato E, Battezzati A, Arcelloni C, Vanzulli A, Testolin G, Pozza G, Del Maschio A, Luzi L. Intramyocellular Triglyceride Content Is a Determinant of in Vivo Insulin Resistance in Humans: a 1H-13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Assessment in Offspring of Type 2 Diabetic Parents. Diabetes. 1999;48:1600–1606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

