Th17: the third member of the effector T cell trilogy
- PMID: 17766098
- PMCID: PMC2288775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.07.020
Th17: the third member of the effector T cell trilogy
Abstract
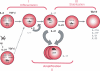
T helper responses have now grown to include three T cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and Th17. Th17 cells have recently emerged as a third independent T cell subset that may play an essential role in protection against certain extracellular pathogens. However, Th17 cells with specificity for self-antigens are highly pathogenic and lead to the development of inflammation and severe autoimmunity. A combination of TGF-beta plus IL-6 and the transcription factors STAT3 and RORgammat were recently described to be essential for initial differentiation of Th17 cells and IL-23 for the later stabilization of the Th17 cell subset. Here, we introduce another player IL-21 produced by Th17 themselves, which plays an important role in the amplification of Th17 cells. Thus, Th17 cells may undergo three distinct steps of development: differentiation, amplification and stabilization in which distinct cytokines play a role.
Figures
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. - PubMed
-
- Kolls JK, Linden A. Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity. 2004;21:467–476. - PubMed
-
- Fort MM, Cheung J, Yen D, Li J, Zurawski SM, Lo S, Menon S, Clifford T, Hunte B, Lesley R, et al. IL-25 induces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and Th2-associated pathologies in vivo. Immunity. 2001;15:985–995. - PubMed
-
- Yao Z, Painter SL, Fanslow WC, Ulrich D, Macduff BM, Spriggs MK, Armitage RJ. Human IL-17: a novel cytokine derived from T cells. J Immunol. 1995;155:5483–5486. - PubMed
-
- Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, Mattson J, Basham B, Sedgwick JD, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ. IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2005;201:233–240. [Of special interest.This paper was the first to establish the pathogenic role of Th17 cells in organ specific autoimmunity. Transfer of IL-23 driven Th17 cells were more efficient in inducing EAE in recipient SJL mice than Th1 cells.] - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

