Heparan sulfate proteoglycans and their binding proteins in embryo implantation and placentation
- PMID: 17766150
- PMCID: PMC2275896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2007.07.013
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans and their binding proteins in embryo implantation and placentation
Abstract
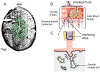
Complex interactions occur among embryonic, placental and maternal tissues during embryo implantation. Many of these interactions are controlled by growth factors, extracellular matrix and cell surface components that share the ability to bind heparan sulfate (HS) polysaccharides. HS is carried by several classes of cell surface and secreted proteins called HS proteoglycan that are expressed in restricted patterns during implantation and placentation. This review will discuss the expression of HS proteoglycans and various HS binding growth factors as well as extracellular matrix components and HS-modifying enzymes that can release HS-bound proteins in the context of implantation and placentation.
Figures
References
-
- Carson DD, Bagchi I, Dey SK, Enders AC, Fazleabas AT, Lessey BA, et al. Embryo implantation. Dev Biol. 2000;223(2):217–37. - PubMed
-
- Hacker U, Nybakken K, Perrimon N. Heparan sulphate proteoglycans: the sweet side of development. Nature reviews. 2005;6(7):530–41. - PubMed
-
- Carter AM. Animal models of human placentation - a review. Placenta. 2007;28(Suppl A):S41–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

