Investigation of the adsorption of PEG1500-12-acyloxystearate surfactants onto phospholipid bilayers: an ellipsometry and cryo-TEM study
- PMID: 17766340
- PMCID: PMC2098744
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.109900
Investigation of the adsorption of PEG1500-12-acyloxystearate surfactants onto phospholipid bilayers: an ellipsometry and cryo-TEM study
Abstract
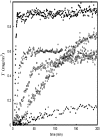
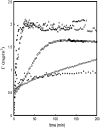
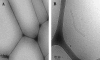
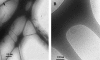
In this article we present a study of a new class of surfactants denoted as PEG1500-12-acyloxystearates, which have potential use as pharmaceutical solubilizers. These amphiphilic molecules present interesting properties with regard to cell damage effects. PEG1500-12-acyloxystearates with C(14) to C(16) acyloxy chains cause little or no damage to red blood and intestinal cells, whereas the surfactants with shorter chains, from C(8) to C(12), induce measurable damage. To start unraveling the reason why there is this rather marked dependence of the cell damage effect on surfactant chain length, we have carried out systematic studies of adsorption properties of the surfactants onto phospholipid bilayers by means of ellipsometry. The rate of incorporation of the surfactants in the lipid membrane decreases with increasing length of the acyloxy chain. Cryo-TEM images strengthen the ellipsometry results by showing that the dissolution of the phospholipid bilayer is slower for the surfactants of the series having longer chains.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Interactions of novel, nonhemolytic surfactants with phospholipid vesicles.Langmuir. 2007 Jun 19;23(13):6956-65. doi: 10.1021/la063700b. Epub 2007 May 22. Langmuir. 2007. PMID: 17516668
-
Phospholipid bilayer-perturbing properties underlying lysis induced by pH-sensitive cationic lysine-based surfactants in biomembranes.Langmuir. 2012 Aug 14;28(32):11687-98. doi: 10.1021/la300626y. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Langmuir. 2012. PMID: 22816661
-
Role of hydrophobic interactions in the adsorption of poly(ethylene glycol) chains on phospholipid membranes investigated with a quartz crystal microbalance.J Phys Chem B. 2009 Mar 19;113(11):3365-9. doi: 10.1021/jp810304f. J Phys Chem B. 2009. PMID: 19227992
-
Mixed micelles and other structures in the solubilization of bilayer lipid membranes by surfactants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Nov 23;1508(1-2):146-63. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(00)00309-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 11090823 Review.
-
Dendrimer-surfactant interactions.Soft Matter. 2014 Apr 28;10(16):2714-27. doi: 10.1039/c3sm53180e. Soft Matter. 2014. PMID: 24668313 Review.
References
-
- Allen, T. M., C. Hansen, F. Martin, C. Redemann, and A. Yau-Yong. 1991. Liposomes containing synthetic lipid derivatives of poly(ethylene glycol) show prolonged circulation half-times in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1066:29–36. - PubMed
-
- Torchilin, V. P. 2001. Structure and design of polymeric surfactant-based drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release. 73:137–172. - PubMed
-
- Ceh, B., M. Wintherhalter, P. M. Frederik, J. J. Vallner, and D. D. Lasic. 1997. Stealth liposomes: from theory to product. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 24:165–177.
-
- Viklund, F. 2003. Surfactants based on natural products. Enzymatic synthesis and functional characterization. PhD thesis. Royal Institute of Technology, Department of Biochemistry, Stockholm, Sweden.
-
- McNamee, C., M. Nilsson, C. von Corswant, and O. Söderman. 2005. Physicochemical characterization of PEG1500-acyloxy-stearate micelles and liquid crystalline phases. Langmuir. 21:8146–8154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

