Effect of lipid peroxidation on the properties of lipid bilayers: a molecular dynamics study
- PMID: 17766354
- PMCID: PMC2098729
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.112565
Effect of lipid peroxidation on the properties of lipid bilayers: a molecular dynamics study
Abstract
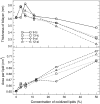
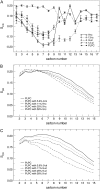
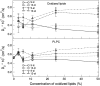
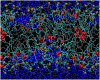
Lipid peroxidation plays an important role in cell membrane damage. We investigated the effect of lipid peroxidation on the properties of 1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (PLPC) lipid bilayers using molecular dynamics simulations. We focused on four main oxidation products of linoleic acid with either a hydroperoxide or an aldehyde group: 9-trans, cis-hydroperoxide linoleic acid, 13-trans, cis-hydroperoxide linoleic acid, 9-oxo-nonanoic acid, and 12-oxo-9-dodecenoic acid. These oxidized chains replaced the sn-2 linoleate chain. The properties of PLPC lipid bilayers were characterized as a function of the concentration of oxidized lipids, with concentrations from 2.8% to 50% for each oxidation product. The introduction of oxidized functional groups in the lipid tail leads to an important conformational change in the lipids: the oxidized tails bend toward the water phase and the oxygen atoms form hydrogen bonds with water and the polar lipid headgroup. This conformational change leads to an increase in the average area per lipid and, correspondingly, to a decrease of the bilayer thickness and the deuterium order parameters for the lipid tails, especially evident at high concentrations of oxidized lipid. Water defects are observed in the bilayers more frequently as the concentration of the oxidized lipids is increased. The changes in the structural properties of the bilayer and the water permeability are associated with the tendency of the oxidized lipid tails to bend toward the water interface. Our results suggest that one mechanism of cell membrane damage is the increase in membrane permeability due to the presence of oxidized lipids.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Molecular dynamics study of oxidized lipid bilayers in NaCl solution.J Phys Chem B. 2013 Jul 18;117(28):8490-501. doi: 10.1021/jp4040612. Epub 2013 Jul 9. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 23800115
-
Lipid peroxidation and water penetration in lipid bilayers: a W-band EPR study.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Feb;1828(2):510-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.09.026. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23036933
-
Effect of oxidation on POPC lipid bilayers: anionic carboxyl group plays a major role.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2023 Jul 12;25(27):18310-18321. doi: 10.1039/d3cp01692g. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2023. PMID: 37401178
-
Peroxidation of liposomal lipids.Eur Biophys J. 2007 Apr;36(4-5):499-515. doi: 10.1007/s00249-007-0146-2. Epub 2007 Mar 23. Eur Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17380326 Review.
-
Understanding membrane remodelling initiated by photosensitized lipid oxidation.Biophys Chem. 2019 Nov;254:106263. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2019.106263. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Biophys Chem. 2019. PMID: 31629920 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid peroxidation modifies the assembly of biological membranes "The Lipid Whisker Model".Front Physiol. 2015 Jan 12;5:520. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00520. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25628570 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Interplay Between Plasma Membrane Lipid Alteration, Oxidative Stress and Calcium-Based Mechanism for Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis From Erythrocytes During Blood Storage.Front Physiol. 2020 Jul 3;11:712. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00712. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32719614 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of aqueous leaf extracts of Chromolaena odorata and Tridax procumbens on doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity in Wistar rats.Porto Biomed J. 2021 Dec 3;6(6):e143. doi: 10.1097/j.pbj.0000000000000143. eCollection 2021 Nov-Dec. Porto Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 34881354 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin resistance and impaired lipid metabolism as a potential link between diabetes and Alzheimer's disease.Drug Dev Res. 2020 Apr;81(2):194-205. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21643. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Drug Dev Res. 2020. PMID: 32022298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CHIP-dependent regulation of the actin cytoskeleton is linked to neuronal cell membrane integrity.iScience. 2021 Jul 17;24(8):102878. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102878. eCollection 2021 Aug 20. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34401662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Markesbery, W. R. 1997. Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 23:134–147. - PubMed
-
- Dexter, D. T., C. J. Carter, F. R. Wells, F. Javoyagid, Y. Agid, A. Lees, P. Jenner, and C. D. Marsden. 1989. Basal lipid peroxidation in Substantia nigra is increased in Parkinson's disease. J. Neurochem. 52:381–389. - PubMed
-
- Mark, R. J., M. A. Lovell, W. R. Markesbery, K. Uchida, and M. P. Mattson. 1997. A role for 4-hydroxynonenal, an aldehydic product of lipid peroxidation, in disruption of ion homeostasis and neuronal death induced by amyloid beta-peptide. J. Neurochem. 68:255–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

