Proteins associated with the Myxococcus xanthus extracellular matrix
- PMID: 17766415
- PMCID: PMC2168726
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01007-07
Proteins associated with the Myxococcus xanthus extracellular matrix
Abstract
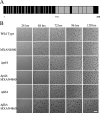
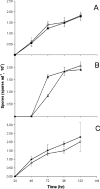
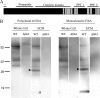
Fruiting body formation of Myxococcus xanthus, like biofilm formation of many other organisms, involves the production of an extracellular matrix (ECM). While the polysaccharide component has been studied, the protein component has been largely unexplored. Proteins associated with the ECM were solubilized from purified ECM by boiling with sodium dodecyl sulfate and were identified by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry of tryptic fragments. The ECM is enriched in proteins of novel function; putative functions were assigned for only 5 of the 21 proteins. Thirteen putative ECM proteins had lipoprotein secretion signals. The genes for many ECM proteins were disrupted in the wild-type (WT), fibA, and pilA backgrounds. Disruption of the MXAN4860 gene had no effect in the WT or fibA background but in the pilA background resulted in a 24-h delay in aggregation and sporulation compared to its parent. The results of this study show that the M. xanthus ECM proteome is diverse and novel.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FibA and PilA act cooperatively during fruiting body formation of Myxococcus xanthus.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Sep;61(5):1283-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05298.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16925559
-
Extracellular biology of Myxococcus xanthus.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010 Mar;34(2):89-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00194.x. Epub 2009 Oct 20. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 19895646 Review.
-
Short-range C-signaling restricts cheating behavior during Myxococcus xanthus development.mBio. 2024 Nov 13;15(11):e0244024. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02440-24. Epub 2024 Oct 18. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39422488 Free PMC article.
-
Sporulation timing in Myxococcus xanthus is controlled by the espAB locus.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Nov;34(4):714-25. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01633.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10564511
-
Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems That Regulate the Temporal and Spatial Expression of Myxococcus xanthus Sporulation Genes.J Bacteriol. 2015 Sep 14;198(3):377-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.00474-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26369581 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biofilm Matrix Proteins.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Apr;3(2):10.1128/microbiolspec.MB-0004-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MB-0004-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26104709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Studies of the Biofilm Matrix including Outer Membrane Vesicles of Burkholderia multivorans C1576, a Strain of Clinical Importance for Cystic Fibrosis.Microorganisms. 2020 Nov 19;8(11):1826. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8111826. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33228110 Free PMC article.
-
The Myxococcus xanthus spore cuticula protein C is a fragment of FibA, an extracellular metalloprotease produced exclusively in aggregated cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028968. Epub 2011 Dec 12. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22174937 Free PMC article.
-
The lethal cargo of Myxococcus xanthus outer membrane vesicles.Front Microbiol. 2014 Sep 9;5:474. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00474. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25250022 Free PMC article.
-
Synergism Between Bacterial GAPDH and OMVs: Disparate Mechanisms but Co-Operative Action.Front Microbiol. 2015 Nov 9;6:1231. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01231. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26617577 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

