Identification of novel surface proteins of Anaplasma phagocytophilum by affinity purification and proteomics
- PMID: 17766422
- PMCID: PMC2168727
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00866-07
Identification of novel surface proteins of Anaplasma phagocytophilum by affinity purification and proteomics
Abstract
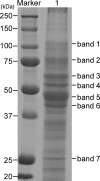
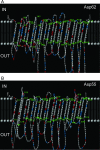
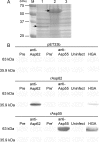
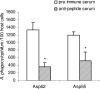
Anaplasma phagocytophilum is the etiologic agent of human granulocytic anaplasmosis (HGA), one of the major tick-borne zoonoses in the United States. The surface of A. phagocytophilum plays a crucial role in subverting the hostile host cell environment. However, except for the P44/Msp2 outer membrane protein family, the surface components of A. phagocytophilum are largely unknown. To identify the major surface proteins of A. phagocytophilum, a membrane-impermeable, cleavable biotin reagent, sulfosuccinimidyl-2-[biotinamido]ethyl-1,3-dithiopropionate (Sulfo-NHS-SS-Biotin), was used to label intact bacteria. The biotinylated bacterial surface proteins were isolated by streptavidin agarose affinity purification and then separated by electrophoresis, followed by capillary liquid chromatography-nanospray tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Among the major proteins captured by affinity purification were five A. phagocytophilum proteins, Omp85, hypothetical proteins APH_0404 (designated Asp62) and APH_0405 (designated Asp55), P44 family proteins, and Omp-1A. The surface exposure of Asp62 and Asp55 was verified by immunofluorescence microscopy. Recombinant Asp62 and Asp55 proteins were recognized by an HGA patient serum. Anti-Asp62 and anti-Asp55 peptide sera partially neutralized A. phagocytophilum infection of HL-60 cells in vitro. We found that the Asp62 and Asp55 genes were cotranscribed and conserved among members of the family Anaplasmataceae. With the exception of P44-18, all of the proteins were newly revealed major surface-exposed proteins whose study should facilitate understanding the interaction between A. phagocytophilum and the host. These proteins may serve as targets for development of chemotherapy, diagnostics, and vaccines.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anaplasma phagocytophilum has a functional msp2 gene that is distinct from p44.Infect Immun. 2004 Jul;72(7):3883-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.3883-3889.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15213131 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Detection and Characterization of p44/msp2 Multigene Family of Anaplasma phagocytophilum from Haemaphysalis longicornis in Mie Prefecture, Japan.Jpn J Infect Dis. 2019 May 23;72(3):199-202. doi: 10.7883/yoken.JJID.2018.485. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30700658
-
Surface-exposed proteins of Ehrlichia chaffeensis.Infect Immun. 2007 Aug;75(8):3833-41. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00188-07. Epub 2007 May 21. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17517859 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms to create a safe haven by members of the family Anaplasmataceae.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Jun;990:548-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07425.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12860688 Review.
-
[Application of affinity chromatography for the purification of the enzymes of lipid metabolism].Seikagaku. 1977;49(12):1335-40. Seikagaku. 1977. PMID: 342645 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Anaplasma phagocytophilum MSP4 and HSP70 Proteins Are Involved in Interactions with Host Cells during Pathogen Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jul 5;7:307. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00307. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28725639 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagosomes induced by a bacterial Beclin 1 binding protein facilitate obligatory intracellular infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 18;109(51):20800-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218674109. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23197835 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Ribosomal Protein RpsB as a Surface-Exposed Protein and Adhesin of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jul 9;2019:9297129. doi: 10.1155/2019/9297129. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31360728 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of Anaplasma phagocytophilum Proteins Involved in Infection of the Tick Vector, Ixodes scapularis.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 4;10(9):e0137237. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137237. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26340562 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the type IV secretion system in different strains of Anaplasma phagocytophilum.BMC Genomics. 2012 Nov 29;13:678. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-678. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23190684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alleman, A. R., A. F. Barbet, H. L. Sorenson, N. I. Strik, H. L. Wamsley, S. J. Wong, R. Chandrashaker, F. P. Gaschen, N. Luckshander, and A. Bjoersdorff. 2006. Cloning and expression of the gene encoding the major surface protein 5 (MSP5) of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and potential application for serodiagnosis. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 35:418-425. - PubMed
-
- Baron, C. 2006. VirB8: a conserved type IV secretion system assembly factor and drug target. Biochem. Cell Biol. 84:890-899. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen, J. D., H. Nielsen, G. von Heijne, and S. Brunak. 2004. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 340:783-795. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

