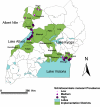
Parasitological impact of 2-year preventive chemotherapy on schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminthiasis in Uganda
- PMID: 17767713
- PMCID: PMC2014753
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-5-27
Parasitological impact of 2-year preventive chemotherapy on schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminthiasis in Uganda
Abstract
Background: Schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminthiasis (STH) are among the neglected tropical diseases in Africa. A national control program for these diseases was initiated in Uganda during March 2003. Annual treatment with praziquantel and albendazole was given to schoolchildren in endemic areas and to adults in selected communities where local prevalence of Schistosoma mansoni in schoolchildren was high.
Methods: The impact of the treatment program was monitored through cohorts of schoolchildren and adults. Their infection status with S. mansoni and STH was determined by parasitological examinations at baseline and at annual follow-ups. The prevalence and intensity of S. mansoni and STH before and after treatment were analyzed.
Results: Two rounds of treatment significantly reduced the prevalence of S. mansoni infection in schoolchildren across three regions in the country from 33.4-49.3% to 9.7-29.6%, and intensity of infection from 105.7-386.8 eggs per gram of faeces (epg) to 11.6-84.1 epg. The prevalence of hookworm infection was reduced from 41.2-57.9% to 5.5-16.1%, and intensity of infection from 186.9-416.8 epg to 3.7-36.9 epg. The proportion of children with heavy S. mansoni infection was significantly reduced from 15% (95% CI 13.4-16.8%) to 2.3% (95% CI 1.6-3.0%). In adults, significant reduction in the prevalence and intensity of S. mansoni and hookworm infections was also observed. More importantly, the prevalence and intensity of both S. mansoni and hookworm infections in the cohorts of newly-recruited 6-year-olds who had never previously received treatment decreased significantly over 2 years: 34.9% (95% CI 31.9-37.8%) to 22.6% (95% CI 19.9-25.2%) and 171.1 epg (95% CI 141.5-200.7) to 72.0 epg (95% CI 50.9-93.1) for S. mansoni; and 48.4% (95% CI 45.4-51.5) to 15.9% (95% CI 13.6-18.2) and 232.7 epg (95% CI 188.4-276.9) to 51.4 epg (95% CI 33.4-69.5) for hookworms, suggesting a general decline in environmental transmission levels.
Conclusion: Annual anthelminthic treatment delivered to schoolchildren and to adults at high risk in Uganda can significantly reduce the prevalence and intensity of infection for schistosomiasis and STH, and potentially also significantly reduce levels of environmental transmission of infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Schistosoma mansoni and soil-transmitted helminths among schoolchildren in An-Nadirah District, Ibb Governorate, Yemen after a decade of preventive chemotherapy.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 25;17(8):e0273503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273503. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36006980 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminth infections among schoolchildren in Burkina Faso.Med Sante Trop. 2016 Aug 1;26(3):267-272. doi: 10.1684/mst.2016.0570. Med Sante Trop. 2016. PMID: 27694082 English.
-
Comparative efficacy of one versus two doses of praziquantel on cure rate of Schistosoma mansoni infection and re-infection in Mayuge District, Uganda.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2013 Jun;107(6):397-404. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/trt024. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2013. PMID: 23596262 Clinical Trial.
-
Schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminthiasis in Rwanda: an update on their epidemiology and control.Infect Dis Poverty. 2017 Mar 1;6(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s40249-016-0212-z. Infect Dis Poverty. 2017. PMID: 28245883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology, of bilharzias (schistosomiasis) in Uganda from 1902 until 2005.Afr Health Sci. 2008 Dec;8(4):239-43. Afr Health Sci. 2008. PMID: 20589131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Five-Year Follow-Up on the Prevalence and Intensity of Infections of Schistosoma mansoni in a Hard-to-Reach District of Madagascar.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2021 Mar 8;104(5):1841-1850. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-1433. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2021. PMID: 33684064 Free PMC article.
-
Differential impact of mass and targeted praziquantel delivery on schistosomiasis control in school-aged children: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Oct 11;13(10):e0007808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007808. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31603895 Free PMC article.
-
Schistosomiasis control in Africa: 8 years after World Health Assembly Resolution 54.19.Parasitology. 2009 Nov;136(13):1677-81. doi: 10.1017/S0031182009991181. Epub 2009 Sep 21. Parasitology. 2009. PMID: 19765347 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Control of neglected tropical diseases needs a long-term commitment.BMC Med. 2010 Oct 29;8:67. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-67. BMC Med. 2010. PMID: 21034473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two-year impact of single praziquantel treatment on infection in the national control programme on schistosomiasis in Burkina Faso.Bull World Health Organ. 2008 Oct;86(10):780-7, A. doi: 10.2471/blt.07.048694. Bull World Health Organ. 2008. PMID: 18949215 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources